
The birds of Louisana include the comical Brown Pelican, photogenic egrets, and more than 485 species!
Louisiana is an absolute haven for birds. Hundreds of wading birds live in this state’s bayous and wetlands, thousands of species migrate through, and stunning Red-headed Woodpeckers call from quaint streets shaded by beautiful Live Oaks.
How many birds in Louisiana have you seen? There are lots of birds to look at in this southern state! But how many were you able to identify?
This list of common backyard and wild birds in Louisiana will help!
Most Common Birds of Louisiana
Louisiana has an abundance of wetlands, forest, and other habitats full of birds.
To create a reliable list of the most common birds in Louisiana, we reviewed eBird sightings from the state, and arranged the birds from most common to least common.
PS! Remember that species on the bottom of the list are common birds too!
To help identify them, we also included information about behavior and field marks.
Northern Cardinal
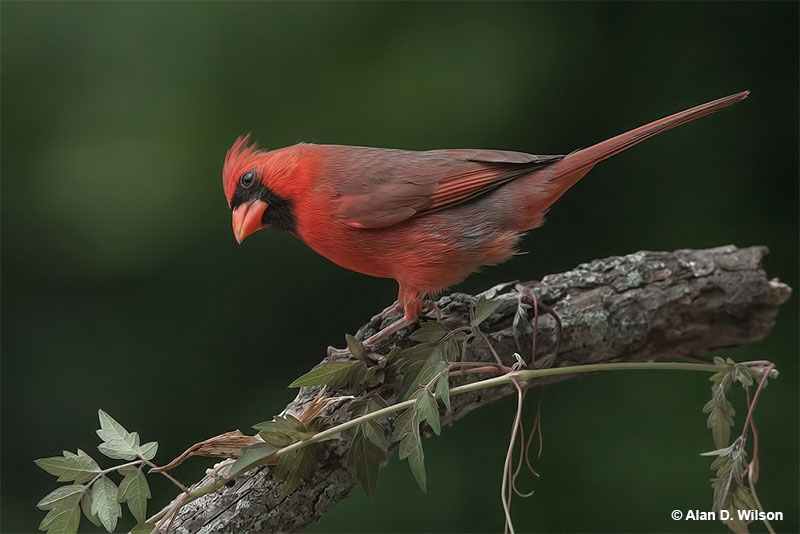

Scientific name: Cardinalis cardinalis
Length: 8.75 inches
Weight: 1.6 ounces
Wingspan: 12 inches
Song: “pichew-pichew-pichew, chew,chew,chew,chew,chew”
Northern Cardinals are medium-sized songbirds with a perky crest and big orange-red beak. Males are bright red with a black throat and face, and have dusky red on their back, wings, and tail.
Female Northern Cardinals are grayish-brown and buff with some black on their face and throat. They also have red highlights in their crest, wings, and long, rounded tail.
This species has short, rounded wings and seems to bounce up and down as they move through the air. In flight, Northern Cardinals also make sharp chip notes.
It eats seeds, insects, and some fruit and is a regular visitor to bird feeders. They forage on and near the ground but males sing from a prominent perch.
This beautiful bird occurs in pairs and nests in bushes and low trees. It is common in the eastern and southwestern USA, southern Ontario, and in Mexico. Northern Cardinals are one of the most beautiful common birds in most states, including Louisiana.
Key Identifications:
- Crested bird with a conical orange-red beak and a black face. Males are red, females are grayish-brown and buff.
- Forages for seeds and insects on and near the ground.
- Makes a cup-shaped nest in bushes and low trees.
- Sings a clear, whistled song of repeated notes. They can sound like “cheer, cheer, chew, chew, chew, chew” or a quick “birdee,birdee,birdee,birdee,birdee“. They also make loud, sharp chip notes.
Blue Jay
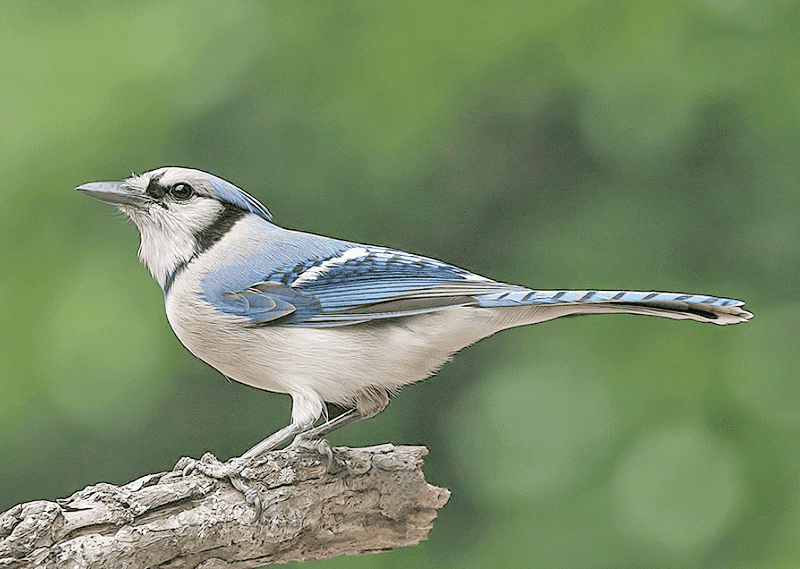
Photograph © Alan Wilson.
Scientific name: Cyanocitta cristata
Length: 11 inches
Weight: 3 ounces
Wingspan: 16 inches
Song: “Nyeah! Nyeah! Nyeah!”
The Blue Jay is a fairly large, crested bird with a straight black bill. Both sexes look alike and are blue above and gray and white below. They also have some small black lines on their faces and a narrow black necklace that goes up to the side of their face and crest.
Blue Jays also have some white markings and black barring in their wings and on their tail. Young birds look like adults but are duller blue.
They make messy cup nests at various heights in a variety of trees.
These social and intelligent birds feed on acorns, nuts, insects, and other small creatures. Like other members of the jay and crow family, they eat the eggs and nestlings of other birds.
The Blue Jay is a common bird of woodlands, forest, and towns east of the Rocky Mountains in the USA and central and southern Canada. Blue Jays are one fo the most common birds of Louisiana.
Key Identifications:
- Crested, fairly large bird with bright blue above and gray below.
- Feeds in trees and at feeders. Eats acorns, nuts, insects and many other food items.
- Makes a messy cup nest of sticks in a tree.
- Very vocal. In flight, Blue Jays often call as they swoop through the trees. They make a variety of sounds and mimic some other birds. Common calls include a nasal and complaining “Nyeah! Nyeah! Nyeah!” and various whistled calls.
Northern Mockingbird
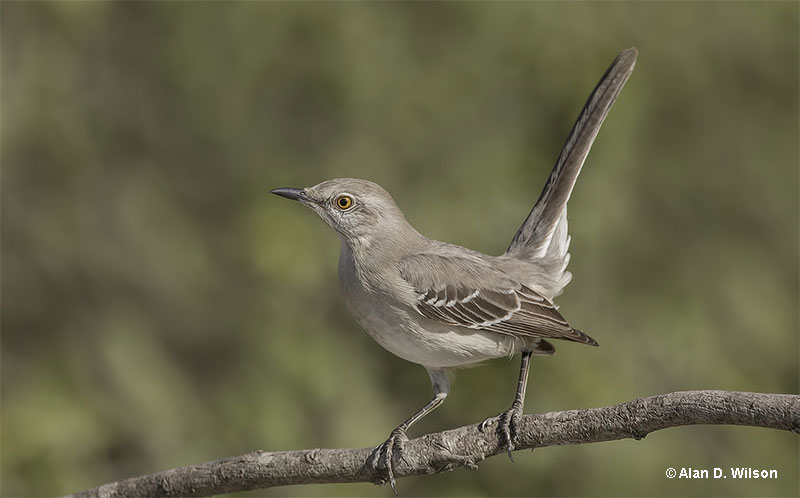

Scientific name: Mimus polyglottos
Length: 10 inches
Weight: 1.7 ounces
Wingspan: 14 inches
Song: “kerdee, kerdee, kerdee…jirdle,jirdle,jidrle…”
The Northern Mockingbird is a pale gray and white bird with a long tail. Around the same size as an American Robin, it has a dark line through a pale eye, a short, slender beak, and two white wing bars.
Both sexes look alike, are gray above, and white and buff below. In flight, this bird shows a blackish tail with white outer feathers and a big white wing patch.
Northern Mockingbirds feed on insects and berries. They forage in open grassy spots, on the ground. These animated birds run and pick bugs from the ground and fly up to catch insects in flight. In winter, they also perch in bushes to feast on berries.
The Northern Mockingbird lives in towns, parks, and other semi-open habitats, and builds cup nests in bushes and low trees. Northern Mockingbirds are common garden birds in much of the eastern and southern USA, southern Ontario, and Mexico.
Key Identifications:
- Vocal, gray and white bird with a small bill, white wing patches, and a long, black and white tail.
- Feeds on the ground in open areas and in bushes. Mostly eats insects and berries.
- Makes a cup nest in a bush or low tree.
- Very vocal. Sings many phrases and mimics many other birds. Some of the more regular phrases sound like, “kerdee, kerdee, kerdee…jirdle,jirdle,jidrle…“. These are interspered with the calls of Blue Jays, woodpeckers, Tufted Titmouse, and various other bird species.
Carolina Wren
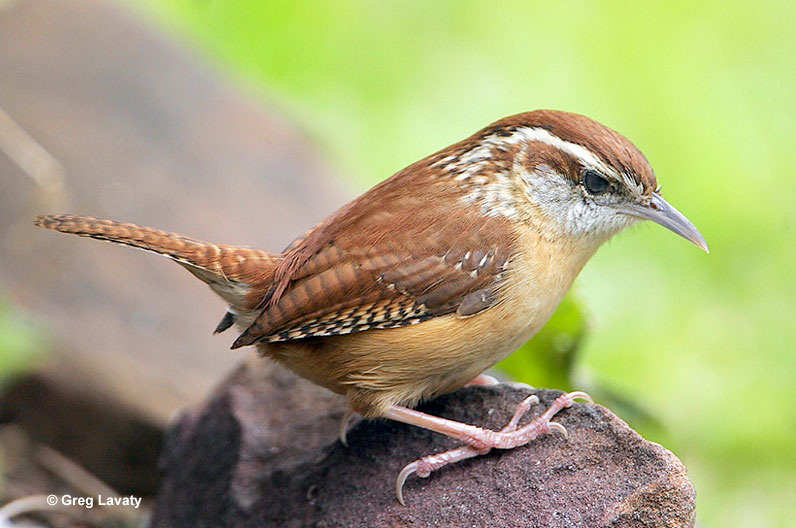

Scientific name: Thryothorus ludovicianus
Length: 5.5 inches
Weight: .74 ounces
Wingspan: 7.5 inches
Song: “teakettle, teakettle, teakettle”
The Carolina Wren is a small, reddish-brown and buff bird with a long, sharp, slightly decurved beak. It has a long, narrow, white eyebrow, a white throat, and some white mottling on its face. Males and females are similar and have black barring on their short wings, long tail, and under the tail.
Juveniles are similar but have paler underparts. This animated and vocal little bird forages for bugs in vine tangles and other dense vegetation. It usually occurs in pairs that can easily hide in the dense vegetation they prefer.
Related: Do you know who’s the state bird of Louisiana?
Carolina Wrens build a domed, cup nest made of sticks and soft vegetation. There is a side entrance and it can be placed in cavities and crevices of stumps, bushes, trees, potted plants, and other structures.
The Carolina Wren lives in vegetated gardens, second growth, parks and similar habitats in much of the eastern USA, parts of southern Ontario, and parts of eastern Mexico. Carolina Wrens are common birds of Louisiana.
Key Identifications:
- Small reddish-brown and buff bird with a long beak and long white eyebrow.
- Feeds on arthropods in dense, tangled vegetation.
- Makes a domed cup nest with a side entrance in crevices, tree cavities, and human-made structures.
- Carolina Wrens fill the garden with loud and melodious songs. One common song sounds like, “teakettle, teakettle, teakettle“. They also make trilled sounds and harsh, nasal calls.
Carolina Chickadee
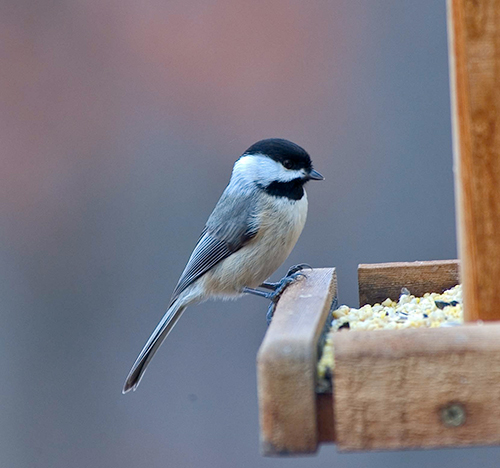

Scientific name: Poecile carolinensis
Length: 4.75 inches
Weight: .37 ounces
Wingspan: 7.5 inches
Song: “see-dee, see-dew”
The Carolina Chickadee is a small, cute, grayish and buff bird with a black cap, black throat, and white face. Males and females look the same and have stubby black beaks, strong, blue-gray legs and feet, and some pale edging on the feathers in their wings and tails.
This small bird mostly feeds on insects and seeds. It finds food by foraging with flocks of other small birds and picking small bugs and other items from bark, foliage, and twigs. Carolina Chickadees often hang upside down from twigs while foraging and are regular visitors to bird feeders.
These fun little birds nest in tree cavities and nest boxes, and live in parks, woodlands, and other habitats. As long as enough trees are present, they also commonly live in urban areas.
The Carolina Chickadee is a permanent resident from Maryland and Ohio west to Texas and south to northern Florida.
Key Identifications:
- The Carolina Chickadee is a small gray and buff bird with a smart black cap, black throat, and white face.
- Feeds on small insects and seeds. A regular visitor to bird feeders.
- Nests in tree cavities and nest boxes.
- Carolina Chickadees are vocal birds that make nasal “chick a dee dee dee” calls, and a high-pitched, “see-dee, see-dew”.
American Crow
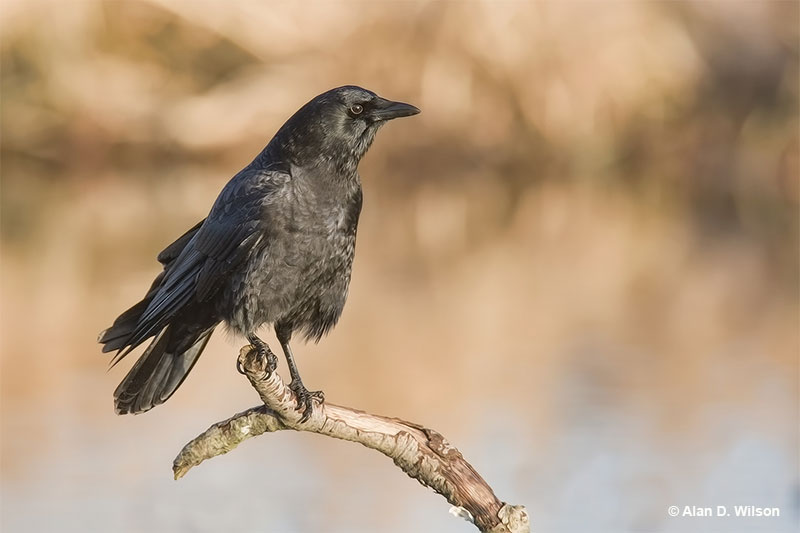

Scientific name: Corvus brachyrhynchos
Length: 17.5 inches
Weight: 1 pound
Wingspan: 39 inches
Song: “Caw! Caw!”
The American Crow is a big, all black bird with a strong, stout bill. In certain lighting, it can have metallic purple and blue iridescence.
Both sexes look the same and have some feathering on their beaks, long, broad wings, and a broad tail.
American Crows have direct flight with strong, steady wing beats. Crows are very social and intelligent birds that are usually seen in flocks. They forage together on the ground or in trees and eat just about anything they can find.
Some of their more regular foods include carrion, fruit, nuts, seeds, insects, and small animals. Like most jays and crow species, they also eat the eggs and nestlings of other bird species.
This species builds bulky stick nests high in trees and lives in most habitats except for high mountains and arid zones.
The American Crow occurs in southern Alaska and much of Canada and the USA.
Key Identifications:
- Big, all black bird with long, broad wing and a broad tail.
- Forages for carrion, fruit, seeds, insects, and small animals.
- Builds a bulky stick nest high in a tree.
- American Crows are very vocal birds. They can make several calls but their most common one is, “Caw! Caw! Caw!”.
Mourning Dove
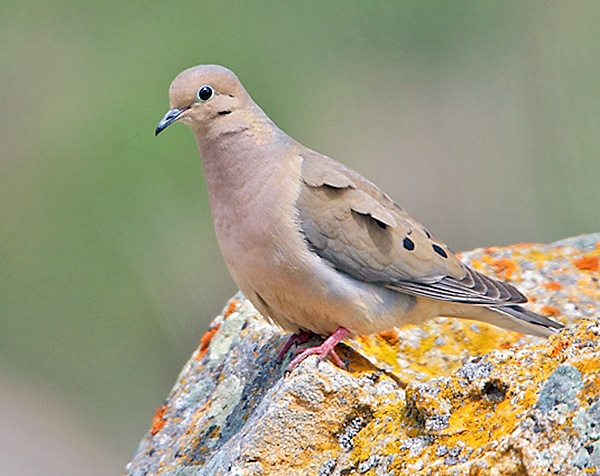

Photograph © Greg Lavaty.
Scientific name: Zenaida macroura
Length: 12 inches
Weight: 4.2 ounces
Wingspan: 18 inches
Song: “hooOOA, hoo, hoo, hoo”
Mourning Doves are medium-sized, grayish-brown doves with long tails. They have small black spots on their wings and a small head with a slender, dark beak.
Males and females also have narrow gray eyerings, a black mark on the face, and pale iridescent gold on the sides of their necks. They look alike except for males having more gray on the head and neck, and more iridescence.
This dove has fairly long wings and swift, direct flight. When flying, it shows black and white in its tail.
The Mourning Dove occurs in woodlands, gardens, on farms, and in urban areas. This common feeder visitor eats seeds and grains. It also forages in open situations, picking food from the ground.
This pleasant dove species can visit a feeder on its own or forage in small flocks. It builds an unkempt stick nest in bushes and trees and is very common throughout the USA, southern Canada, and Mexico.
Key Identifications:
- Plain brown and gray dove with a long, pointed tail.
- Feeds on seeds at feeders and on the ground in open areas.
- Makes a small, messy nest of sticks in trees.
- Sings a sad and owl-like “hooOOA, hoo, hoo, hoo”.
Red-bellied Woodpecker
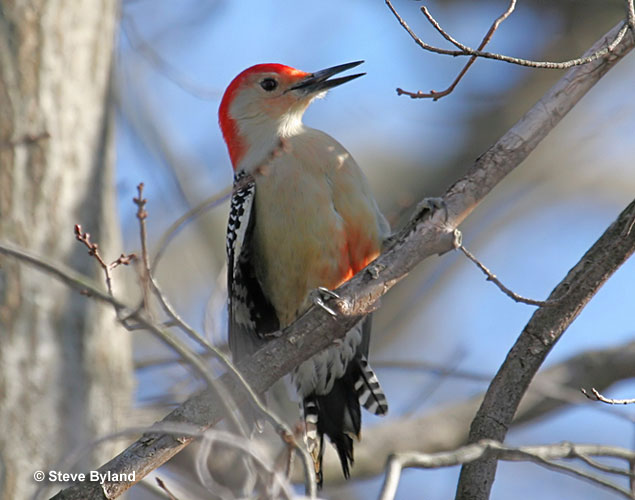

Scientific name: Melanerpes carolinus
Length: 9.25 inches
Weight: 2.2 ounces
Wingspan: 16 inches
Song: “Qwerr!”
Red-bellied Woodpeckers are medium-sized with black and white barring on their back and wings. They have a long beak and pale gray underparts with a small red patch on the belly.
Males have red on the head from the bill to the back of the neck (the nape). Females have an orange-red spot above their bill and red on the back of their head. Both sexes have a mostly white rump and central tail feathers.
This woodpecker species has long wings and “undulating” flight where it moves up and down as it flies. In flight, Red-bellied Woodpeckers show a small white patch in their wings.
The Red-bellied Woodpecker lives in wooded habitats. It eats nuts, seeds, insects, fruit, and can attack nestlings of other species. It also visits bird feeders.
This striking woodpecker occurs in pairs and nests in tree cavities high above the ground. It is common in the eastern USA and parts of southern Ontario.
Key Identifications:
- Grayish woodpecker with black and white barring above, and red on the top of the head and back of the neck.
- Forages for seeds, nuts, insects and other food on trunks and branches.
- Nests in a tree cavity, high overhead.
- Makes a loud exclamation, “Qwerr!“. It also makes other, briefer and quieter “chug” calls.
Great Egret
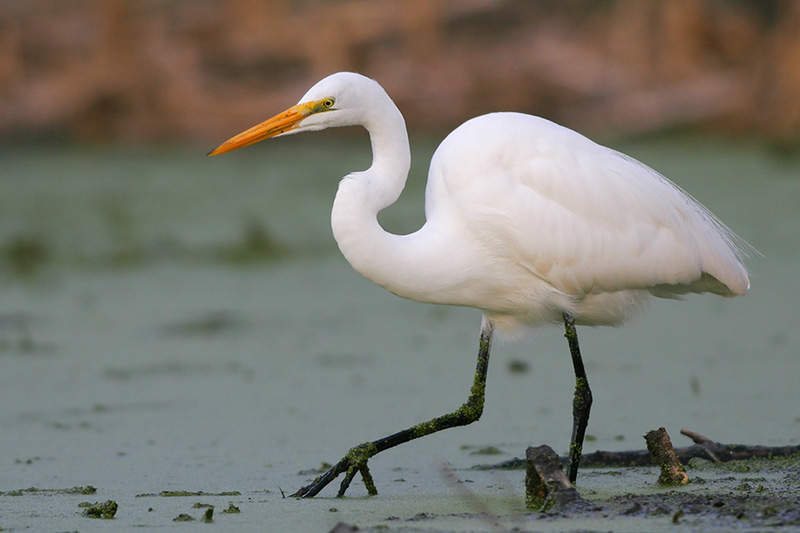

Photograph © Greg Lavaty
Scientific name: Ardea alba
Length: 39 inches
Weight: 1.9 pounds
Wingspan: 51 inches
Song: “koorr”
The Great Egret is a big, white heron with a long neck, and long dark legs and feet. Both sexes look similar and have long, sharp yellow beaks, and pale eyes.
During breeding season, they have long, elegant white plumes on their backs, and greenish skin in front of their eyes.
In flight, this large waterbird shows long, broad wings and a short, broad tail. Its legs trail out behind it and the neck is tucked in.
Great Egrets feed on fish, frogs, snakes, and other small animals that venture too close, birds and rodents included.
Great Egrets nest in colonies and build big, messy, stick nests. It is common in wetlands in much of the USA, parts of southern Canada, and many other parts of the world.
Key Identifications:
- Big white bird with a long neck, yellow beak, and dark legs and feet.
- Feeds in and near wetlands, on the ground. Catches fish and small animals with its long, sharp beak.
- Makes bulky stick nests in colonies.
- Great Egrets make deep, croaking sounds, especially when taking flight. “koorr…koorr“
Downy Woodpecker
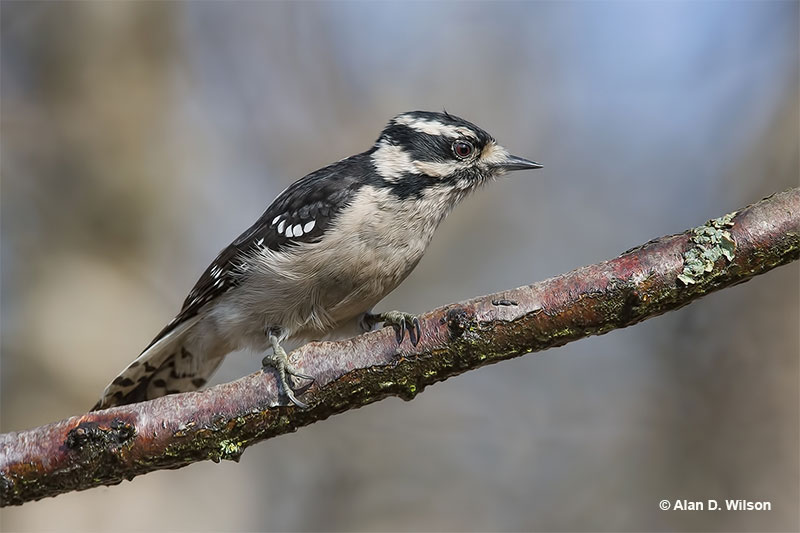

Scientific name: Dryobates pubescens
Length: 6.75 inches
Weight: .95 ounces
Wingspan: 12 inches
Song: “Pik! Ch,ch,ch,ch,ch,ch,ch!”
The Downy Woodpecker is a small black and white woodpecker with a short, black beak. They are patterned black and white above and have white backs and white underparts. Both sexes look alike except that males have a small, bright red patch on the top back part of their head.
Young birds look like adults but have a reddish patch on the top of their heads. Downy Woodpeckers also have a few small black marks in their white outer tail feathers and a small white tuft at the base of their beak.
Downy Woodpeckers eat insects, other small creatures, seeds, and small fruits. It pecks into live and dead wood and often forages on smaller branches and twigs. These friendly little woodpeckers are also common feeder birds.
They nest in tree cavities and live in gardens and a wide variety of woodlands. We see Downy Woodpeckers in much of Canada and the USA but not in arid habitats.
Key Identifications:
- Smallest woodpecker in North America. Mostly black and white with a short, black beak.
- Forages on trees, in bushes, and at feeders for insects, seeds, and suet.
- Nests in tree cavities.
- The Downy Woodpecker makes sharp “pik!” calls and also has a trilled call, “Ch,ch,ch,ch,ch,ch,ch!“.
Red-winged Blackbird
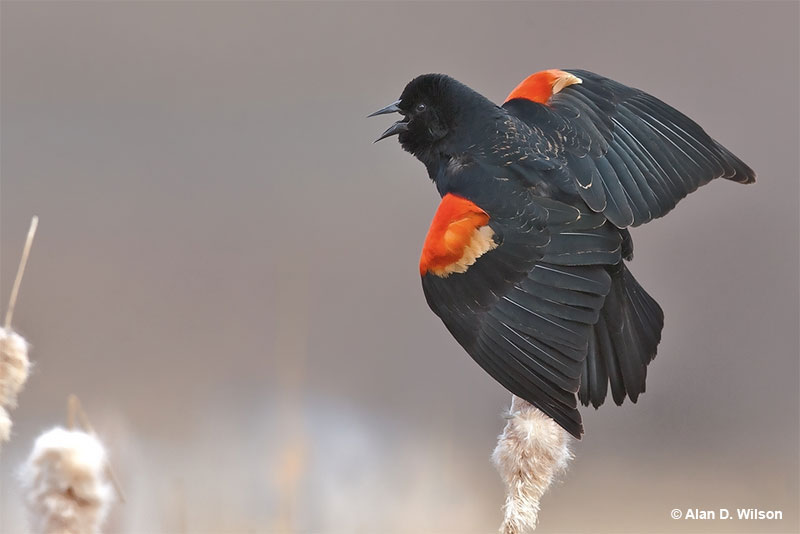

Scientific name: Agelaius phoeniceus
Length: 8.75 inches
Weight: 1.8 ounces
Wingspan: 13 inches
Song: “kan-keree!”
The Red-winged Blackbird is a medium-sized blackbird species with a sharp, all-black bill. Males also have a scarlet patch with a pale yellow border on the shoulder of each wing.
Female Red-winged Blackbirds are dark, heavily streaked, brownish-gray birds with an orange-buff eyebrow and throat. She can also have a little bit of dingy red on her shoulder.
Red-winged Blackbirds often flock together and can form very large groups in the winter. They feed on seeds, grain, and insects found on lawns, in marshes, farm fields, and other open habitats.
This species builds a cup nest made of leaves and dead stems in a bush or other low vegetation in a marsh, park, or brushy field.
Red-winged Blackbirds are very common birds that live in all sorts of open habitats. We see them in parks, farming areas, and marshes in much of Canada, the USA, Mexico, and parts of the Central America.
Key Identifications:
- Males are medium-sized blackbirds with bright red patches on their wings. Females are heavily streaked, have a sharp black beak, and buff on the head.
- Feeds on seeds, grain, and insects on the ground in many open habitats.
- Builds a cup nest in a bush or other low vegetation.
- Red-winged Blackbirds often call. Males sing a loud, “kan-keree!” and both sexes also make “check!” calls and a high-pitched whistle-like sound.
Tufted Titmouse
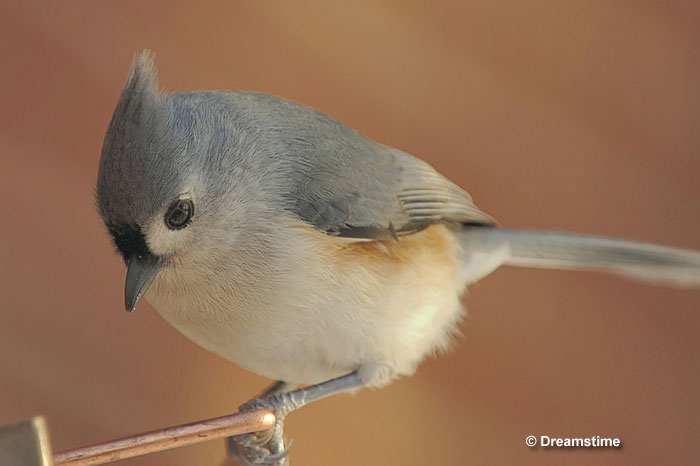

Scientific name: Baeolophus bicolor
Length: 6.5 inches
Weight: .75 ounces
Wingspan: 9.75 inches
Song: “peter peter peter”
The Tufted Titmouse is a small, crested, blue-gray bird with a white face. Males and females look the same and have a small black mark above their stubby black beak. They also have pale underparts with peach-orange flanks.
These cute little birds occur in small groups that forage for insects and seeds in parks and woodlands. They move through the trees and use their bills to pick food from leaves, bark, and branches. Tufted Titmouse are also regular visitors to bird feeders.
These small birds nest in woodpecker holes and other cavities in dead trees, and can also use nest boxes.
We find the Tufted Titmouse in hardwood forests and forested urban areas. They are often heard before they are seen and flock with other small birds. When they see a predator, they are some of the first birds to harass it.
The Tufted Titmouse occurs in the eastern USA and some parts of southeastern Canada.
Key Identifications:
- Small, crested blue-gray bird with pale underparts and a white face.
- Feeds on seeds and insects and visits feeders.
- Nests in tree cavities and nest boxes.
- The Tufted Titmouse is a very vocal bird. It gives constant whistled calls over and over, “peter peter peter“.
Yellow-rumped Warbler

Scientific name: Setophaga coronata
Length: 5.5 inches
Weight: .42 ounces
Wingspan: 9.25 inches
Song: “si,sit,sit,sit,sit,sue,sue,sue”
The Yellow-rumped Warbler is a small, blue-gray songbird with a yellow rump, crown, and yellow patches on each side of its breast. It also has two white wing bars, dark marks on the back, and white underparts with blackish markings on its breast and sides.
In summer, this species has a blackish face and white markings above and below the eyes. Females are like males but duller. In winter, both sexes of Yellow-rumped Warblers are duller and have more brownish plumage.
The western subspecies have a yellow throat and more white in the wings.
This species feeds on insects and small berries. It picks food from vegetation and briefly flies into the air to catch bugs in flight.
Yellow-rumped Warbler builds small cup nests in conifers in Canada and the northeastern and western USA. They spend the winter in semi-open habitats from the southern USA to Central America.
Key Identifications:
- Small songbird with two pale wing bars and yellow patches on the rump, each side of its breast, and crown.
- Feeds on insects and small berries.
- Builds cup nests in conifers in northern and montane forests.
- The Yellow-rumped Warbler makes a sharp call note, “chup!”, and sings a brief and easy-going warbling song, “si,sit,sit,sit,sit,sue,sue,sue”.
House Sparrow
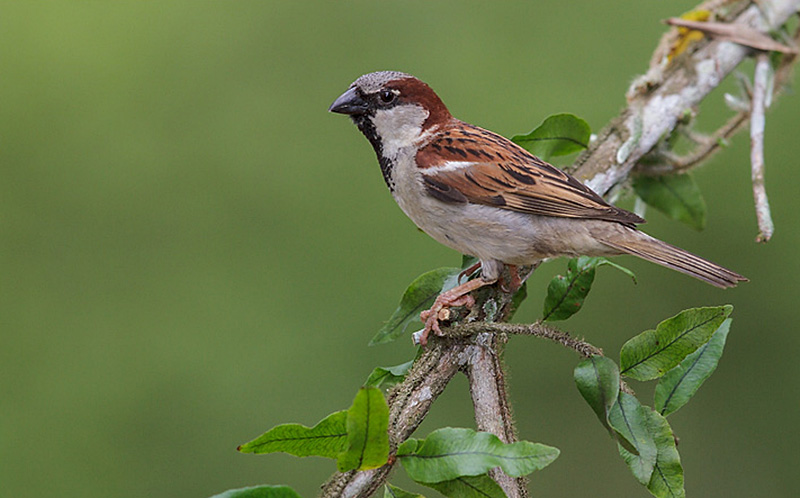

House Sparrow (Passer domesticus) perched on a branch in the Atlantic rainforest of southeast Brazil.
Scientific name: Passer domesticus
Length: 6.25 inches
Weight: .98 ounces
Wingspan: 9.5 inches
Song: “see,chirrup,see,chirrup,see,chirrup”
House Sparrows are small, plump gray and brown birds with conical, finch-like beaks. Males have a gray and rufous head with pale cheeks, and black near their eyes and on their throat.
The rest of their underparts are gray and they have brown, streaked backs with rufous highlights. They also have a white mark in the shoulder of each wing and a grayish rump and tail.
Females are plainer brown and buff, have paler beaks, and buff eyebrows.
House Sparrows feed on seeds, grain, and insects. They are regular visitors to bird feeders and often dominate other smaller species.
They also forage on the ground in farmlands, parks, urban areas, and other open situations.
The House Sparrow nests in cavities. When searching for suitable nesting sites, they can kill and remove the eggs and young of smaller species like Eastern Bluebirds.
House Sparrows usually live near people and occur in most of North America, including Louisiana.
Key Identifications:
- Brown and gray sparrow with a bold pattern on its head.
- Feeds on seeds, grain, and insects at feeders and on the ground in urban areas and farmlands.
- Nests in tree cavities, including nest boxes.
- This species is vocal and often makes short chirping calls. Its song is a friendly series of chirping sounds, “see,chirrup,see,chirrup,see,chirrup”.
Great Blue Heron
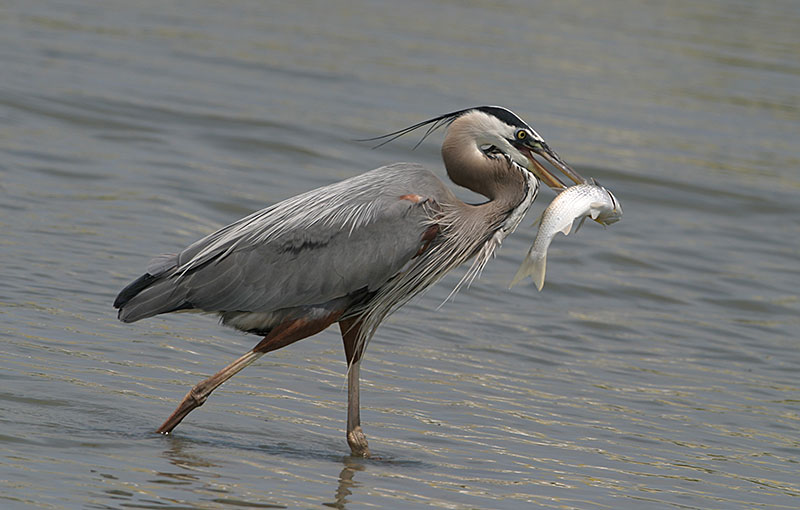

Scientific name: Ardea herodias
Length: 46 inches
Weight: 5.3 pounds
Wingspan: 72 inches
Song: “Grunk! Grunk!”
The Great Blue Heron is a large, gray and pale brown heron with a long neck and legs. It has a strong, yellowish beak, black and white head with a wispy black crest, and rufous thighs.
Both sexes are alike and have pale bellies and black flanks. Juveniles have streaked underparts.
In flight, they make slow, deep flaps with long, broad gray and black wings. In Southern Florida and the Caribbean, Great Blue Herons are all white and sometimes considered a separate species, the Great White Heron.
These powerful herons feed on fish and small animals such as rats, snakes, and birds.
Great Blue Herons build messy, stick nests and breed in colonies, often in swamps.
We find these impressive birds in and near various wetlands in large parts of Canada, the USA, and the Caribbean.
Key Identifications:
- Huge gray and pale brown wading bird with a thick, yellowish beak and a wispy crest. In southern Florida, it is all white but still has a crest and a strong yellowish beak.
- Stalks and preys on fish and small animals.
- Builds messy stick nests and breeds in colonies.
- Great Blue Herons aren’t all that vocal. When taking flight they make a croaking sound, “Grunk! Grunk!“.
European Starling

Photograph © Greg Lavaty.
Scientific name: Sturnus vulgaris
Length: 8.5 inches
Weight: 2.9 ounces
Wingspan: 16 inches
Song: “tiktiktitZHREEree..tiktiktik..ZHREE”
European Starlings are plump, short-tailed birds with long sharp beaks and longish, pointed wings. In summer, they have yellow beaks, glossy black plumage with purple and green highlights, and some small white spots.
Males and females are similar, but males have less spotting and glossier plumage. In winter, they have black beaks, white spots, and more reddish colors in their wings.
Young starlings are shaped like adults but are grayish birds with a dark beak and a pale throat.
This species feeds on a variety of insects, fruit, and seeds. They can dominate bird feeders and are common species in urban areas, parks, farmlands, and other open habitats.
This European Starling builds a soft cup nest in a tree cavity, nest box, or suitable cavity in other structures.
European Starlings flock with each other and blackbird species, especially during the winter. They live across a large part of Canada and the USA.
Key Identifications:
- Rotund, short-tailed bird with a long, sharp bill, and pointed wings. Glossy black with some spotting in the summer and blackish with heavy white spotting and streaking in the winter.
- Feeds on seeds, fruit, and insects. Visits feeders and forages on the ground in flocks.
- Builds a soft cup nest in nest boxes and other cavities.
- The European Starling makes a wide variety of mechanical and whistled sounds. They also mimic other birds and sounds in their environment. They sing long, jumbled mechanical-sounding songs, “tiktiktitZHREEree..tiktiktik..ZHREE”.
Ruby-crowned Kinglet
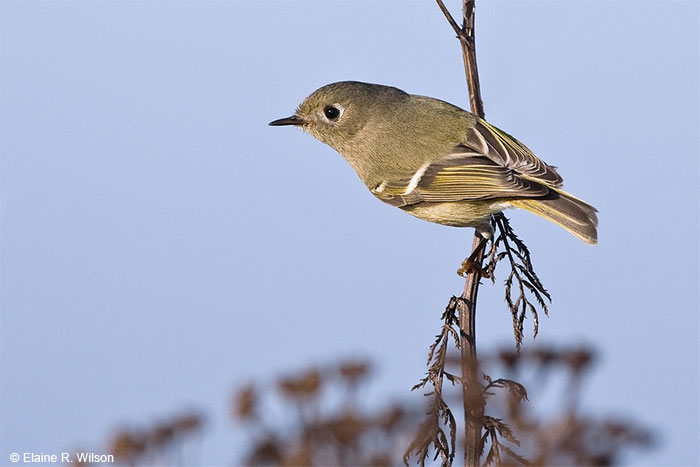

Scientific name: Corthylio calendula
Length: 4.25 inches
Weight: .23 ounces
Wingspan: 7.5 inches
Song: “seetseetseet, reardidehdidid, ridiDEEP,ridiDEEP,ridiDEEP!”
Ruby-crowned Kinglets are tiny, grayish-olive birds with small, slender beaks. They have broken white eyering and dark wings with yellowish-white edging on their feathers.
Both sexes look very similar and also have two white wing bars, the lower wing bar much more obvious than the upper one. Males also have a hidden, bright red or orange crest revealed in displays and aggressive situations.
The Ruby-crowned Kinglet is an active bird that rarely sits still. It feeds on small bugs, spiders, and insect eggs that it finds in conifers, bushes, and trees. They can forage at any height, often hover to pick food off foliage, and usually occur in flocks with other small birds.
Ruby-crowned Kinglets breed in coniferous forests in Alaska, Canada, parts of the northern USA, and the western USA. They spend the winter in parks and woodlands in much of the eastern, southern, and western USA, and Mexico.
Key Identifications:
- Tiny, grayish-olive bird with a broken eyering, two pale wing bars (the lower one more obvious), and a hidden red crest.
- Feeds on small arthropods and insect eggs in bushes and trees.
- Makes a small, rounded cup nest out of moss, lichens, and other soft materials high in a spruce or other conifer.
- Sings a cheerful and surprisingly loud, “seetseetseet, reardidehdidid, ridiDEEP,ridiDEEP,ridiDEEP!”.
Eastern Bluebird
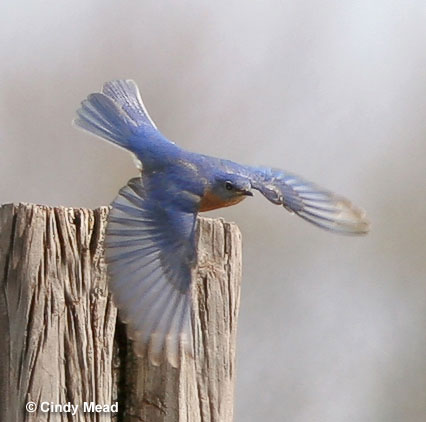

Scientific name: Sialia sialis
Length: 7 inches
Weight: 1.1 ounces
Wingspan: 13 inches
Song: “fer fer chidip fer”
The Eastern Bluebird is a rather small, blue and white bird with orange on the side of its neck, throat, breast, and flanks. The male has beautiful pastel blue upperparts, and a white belly and undertail.
Females have blue-gray upperparts, a broken white eyering, and some white on the throat.
Juveniles are gray-brown with some blue and pale spotting.
The Eastern Bluebird feeds on insects, fruit, and occasional seeds. It snatches insects in flight, picks them from leaves while hovering, and flies down to meadows and grassy areas to catch them on the ground.
Flocks of Eastern Bluebirds feed on small fruits by perching in fruiting trees and picking them from vegetation.
Eastern Bluebirds make a shallow cup nest out of grass inside a tree cavity or nest box.
This beautiful bird lives in open and semi-open habitats in southern Canada and the USA east of the Rocky Mountains. They also live in the mountains in Mexico and northern Central America (including Louisiana).
Key Identifications:
- Smallish blue and white bird with orange on their throat, breast, and flanks.
- Forages for insects and small fruit.
- Makes a shallow cup nest out of grass in a nest box or tree cavity.
- Has short melodious calls, “jeer” and a song of similar melodious notes, “cheweer chewit cherwit”.
Turkey Vulture
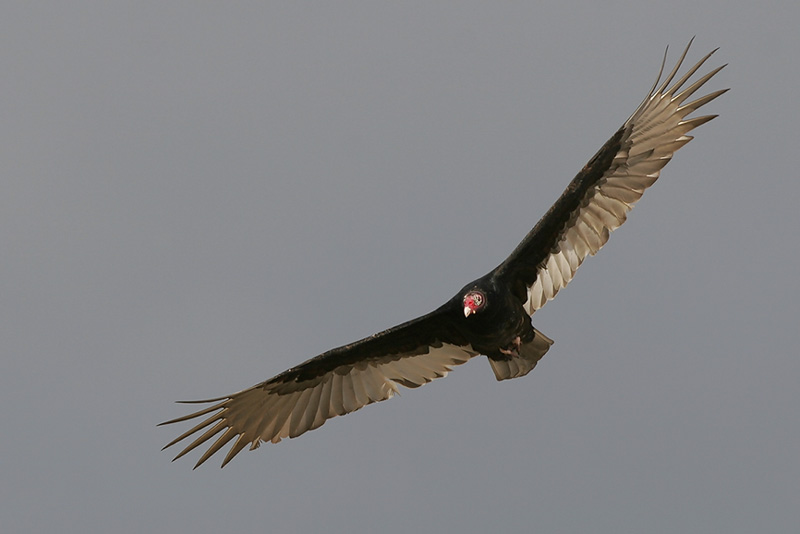

Scientific name: Cathartes aura
Length: 26 inches
Weight: 4 pounds
Wingspan: 67 inches
Song: “hisss”
The Turkey Vulture is a big, dark brownish-black raptor with a small red head and long, broad wings. Males and females look alike and also have a longish tail.
In flight, the way Turkey Vultures soar is one of the best ways to recognize them. They fly with their wings held in a “V” shape and, when gliding, often rock back and forth.
Their flight feathers are also paler than the rest of their wings, but they lack the Black Vulture’s white wing patch.
Turkey Vultures are scavengers, and most of their diet is carrion. They eat road kill and a wide variety of dead animals. This species forages over every type of habitat and can also fly over urban areas.
It lays two eggs on the ground in caves and hollow logs.
The Turkey Vulture lives in southern Canada and in most of the USA south to southern Argentina.
Key Identifications:
- Big, dark raptor with a small red head that soars with long wings held in a “V”.
- Feeds on dead animals.
- Nests on the ground in caves and hollow logs in secluded areas.
- Turkey Vultures rarely call and mostly make hissing sounds at their nest.
Fish Crow
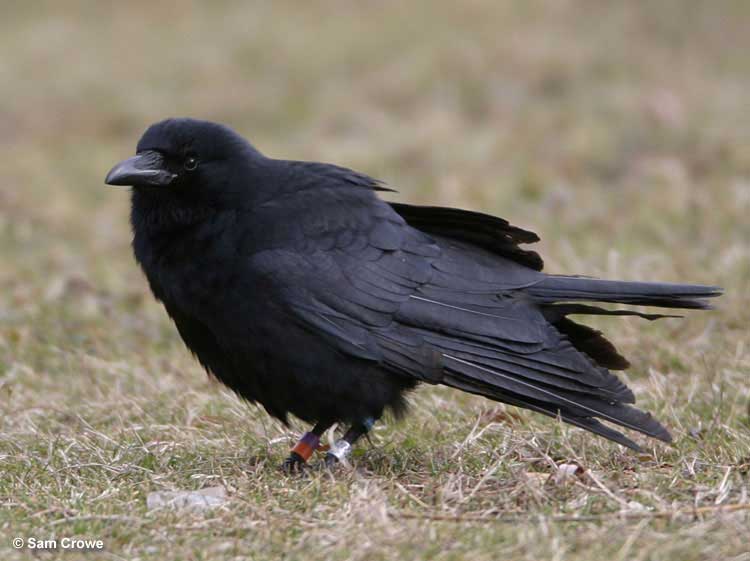

Scientific name: Corvus ossifragus
Length: 15 inches
Weight: 10 ounces
Wingspan: 36 inches
Song: “cuh”
The Fish Crow is a large, all-black bird with a stout, black beak. Both males and females look the same and have some feathers on top of their bill, long wings, and a broad tail. In certain lighting, they also show some dark blue and purple highlights.
This species feeds on small creatures and a wide variety of food items found in coastal habitats and in other wetlands. It also scavenges for carrion and preys on eggs and nestlings of other bird species.
In particular, Fish Crows are important predators at nesting colonies of waterbirds.
After breeding, Fish Crows form large flocks and, in many places, they have become adapted to living in urban areas. These birds have become used to people but don’t usually visit feeders.
They build large, messy stick nests high in trees and only live in coastal areas and wetlands in the eastern USA.
Key Identifications:
- Large black bird with long wings and a broad tail.
- Feeds on carrion, small animals, and many other food items.
- Makes messy stick nests in trees.
- Fish Crows are vocal, social birds. Their nasal call is the best way to separate them from the American Crow. It sounds like, “cuh, cuh“.
Ruby-throated Hummingbird
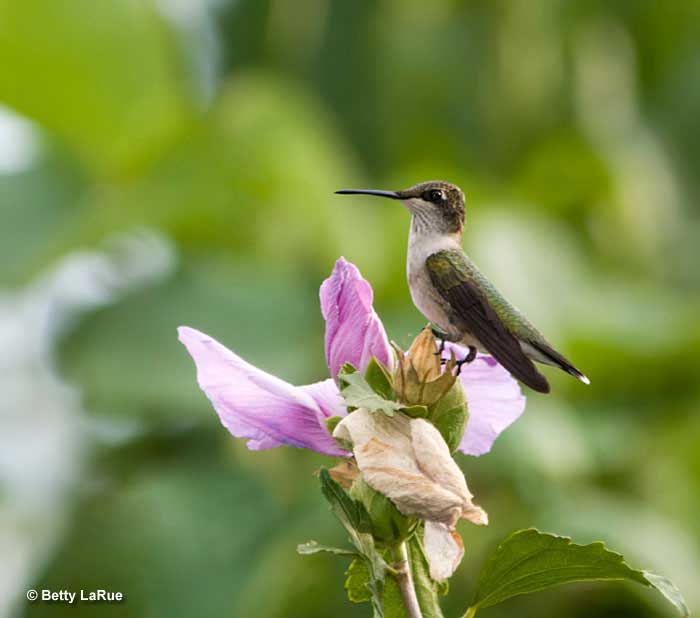

Scientific name: Archilochus colubris
Length: 3.75 inches
Weight: .11 ounces
Wingspan: 4.5 inches
Song: “tik,chickechikchicktiktik”
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds are tiny birds with long, sharp, needle-like beaks. Males are green above and grayish-green below with a broad white semi-collar on their breast and neck. They also have a dark, forked tail, and a glittering orange-red throat.
Females have a pale throat, a small white spot behind each eye, and black and white on the tip of their tail.
This hummingbird species feeds on nectar and tiny insects. It takes nectar from a variety of small flowers and visits hummingbird feeders. They also catch small insects in flight.
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds make small cup nests out of lichen, spider webs, and plant matter. The female constructs the nest on a branch of a tree, often high up.
Ruby-throated Hummingbirds breed in woodland habitats in central and southeastern Canada, and the eastern USA. We often see them in gardens and at hummingbird feeders, especially during migration.
They migrate to Mexico and Central America for the winter.
Key Identifications:
- Tiny greenish bird with a long, straight beak. Males have glittering red throats and females have pale throats and a small white spot behind the eye.
- Takes nectar from flowers, visits hummingbird feeders, and eats tiny insects.
- Makes a small cup nest of lichen, spider webs, and plant matter in a tree.
- The Ruby-throated Hummingbird makes lots of chipping and sputtering calls. They often sound like, “tik,chickechikchicktiktik”.
Blue-gray Gnatcatcher
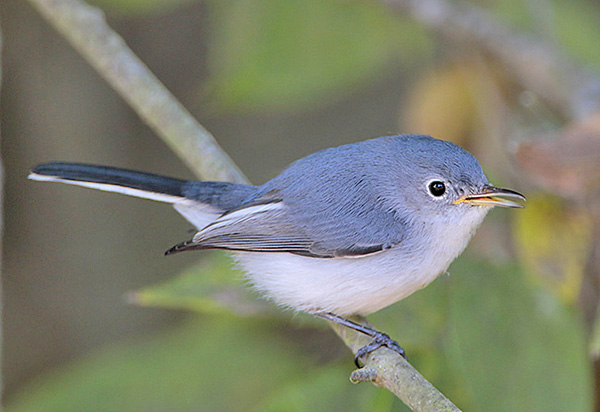

Photograph © Greg Lavaty.
Scientific name: Polioptila caerulea
Length: 4.5 inches
Weight: .21 ounces
Wingspan: 6 inches
Song: “nheah, sip, nheah”
The Blue-gray Gnatcatcher is a tiny, pale gray and white bird with a slender beak. They are blue-gray above and pale gray below with a white eyering. They also have some white edging in their short wings and a longish, black and white tail.
Both sexes look similar, except that males have a small black line above their eyes. This species feeds on small insects that it catches in bushes and deciduous trees.
It forages by quickly moving through vegetation and picking bugs from vegetation. They can also fly out to catch insects in flight.
Blue-gray Gnatcatchers make a small cup nest out of lichens and spider webs, usually high in a tree. They live in hardwood forests and are summer residents in parts of southeastern Canada, the eastern USA, and also live in some western states.
They also breed in Mexico and winter from the southern USA to the Caribbean and Honduras.
Key Identifications:
- Tiny pale blue-gray and white bird with a slender beak and longish black and white tail.
- Actively forages for insects.
- Makes a small pale cup nest high in trees.
- Blue-gray Gnatcatchers are quite vocal and make nagging nasal calls. Their most common call sounds like, “nheah, sip, nheah”. They also sing a scratchy song with nasal and tinkling sounds.
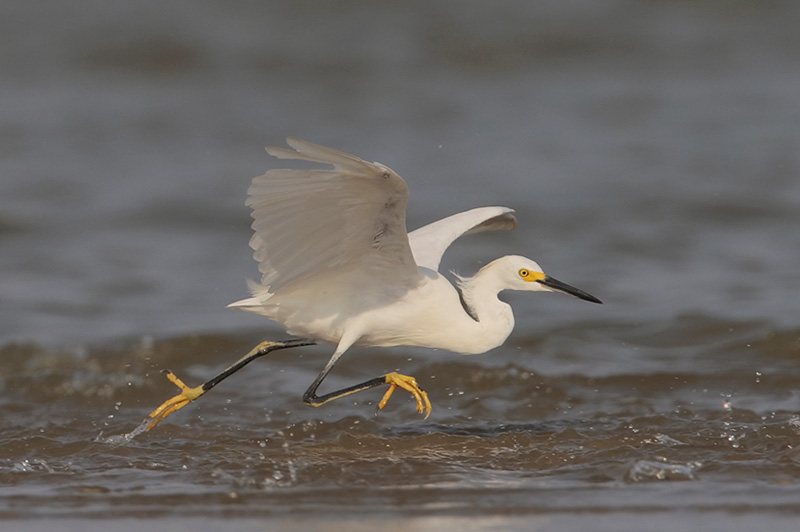
Snowy Egret

Scientific name: Egretta thula
Length: 39 inches
Weight: 1.9 pounds
Wingspan: 51 inches
Song: “rahh”
The Snowy Egret is a medium to large, elegant white bird with a long, slender black bill, and long black legs with yellow feet. Both sexes look alike and have some yellow skin in front of yellow eyes, a wispy white crest, and elegant plumes on their breast and lower back.
Snowy Egrets fly with long, broad wings, hold their necks tucked in, and have slow, deep wing beats.
This beautiful heron feeds on small fish, insects, and other small aquatic creatures. It catches food by wading in or near water, waiting until prey comes close, and quickly striking out with its long bill. In shallow water, it also briefly runs after small fish to catch them.
Snowy Egrets breed in colonies and make messy stick nests in trees and bushes. They live in coastal areas and along marshes, lakes, and rivers in much of the USA and Central and South America.
Key Identifications:
- Medium-sized elegant white heron with a long, black beak, and long black legs with yellow feet.
- Forages for small fish and other creatures by wading in or near shallow water and quickly snatching them with its beak.
- Breeds in colonies and makes a messy stick nest in trees and bushes, usually on islands or over water.
- Snowy Egrets are not very vocal birds. They usually make a croaking call when taking flight. It sounds like, “rahh”.
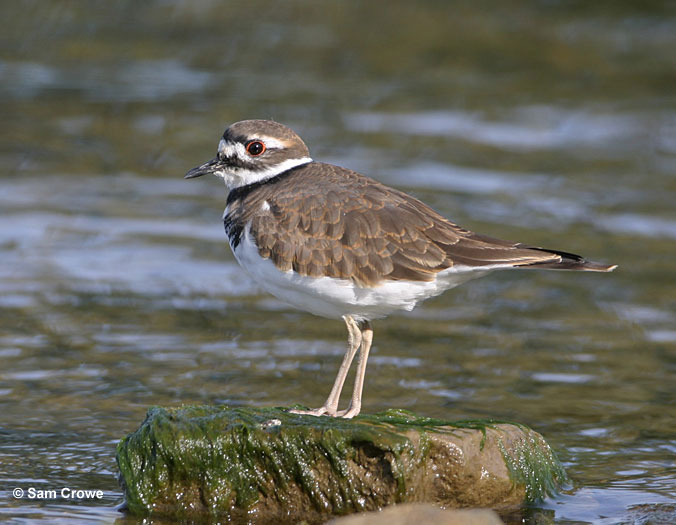
Killdeer

Scientific name: Charadrius vociferus
Length: 10.5 inches
Weight: 3.3 ounces
Wingspan: 24 inches
Song: “tideer, tideer, tideer, tideer”
The Killdeer is a fair-sized, slender plover that is dark brown above and white below. They have two black bands on their breast, a patterned, black, white, and dark brown face, and a longish, orange tail.
Both sexes look alike and also have a slender, black bill, narrow, red-orange eyerings, and long, pale legs. In flight, we can see a white stripe in each of their long, dark wings, and a black tip on their long, wedge-shaped, orange tail.
Killdeers often fly high overhead in fast, direct flight, but we usually see them foraging on the ground. They pick insects, other small creatures, and seeds from the edges of wetlands and other, open grassy areas.
This species lays its camouflaged eggs on the ground, in gravel and open fields. When people and pets approach too close, they give loud calls and pretend to have a broken wing.
The Killdeer lives in large parts of Canada, the USA, Mexico, and also Louisiana.
Key Identifications:
- Fair-sized plover with two black breast bands and a wedge-shaped orange tail with a black tip.
- Picks seeds and small creatures from open ground.
- Lays camouflaged eggs on the ground, in gravel and open fields.
- Very vocal and sounds like it says its name, “tideer, tideer, tideer, tideer”.
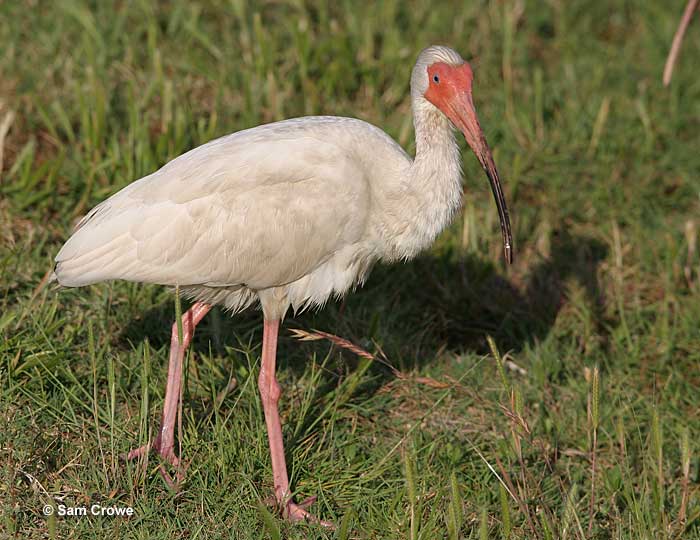
White Ibis

Scientific name: Eudocimus albus
Length: 25 inches
Weight: 2 pounds
Wingspan: 38 inches
Song: “whaah”
The White Ibis is a fair-sized, white waterbird with a long, decurved red bill, and long red legs. Males and females look alike and also have a bare red face, and pale eyes. Although their bill is red, because they use it to probe in the muddy ground, half the beak often looks blackish.
In flight, these birds show long, broad wings with black wingtips and short, broad tails. Young birds have grayish-brown on their head and neck, and dark brown on the back, wings, and tail.
The White Ibis often occurs in flocks of a dozen or so birds. They feed on frogs and other small aquatic creatures as well as other food they find and catch. This bird forages by wading in shallow water or other wet places and probing the wet ground with its beak.
It nests in colonies and builds a messy stick nest in trees and thickets. These social birds are common species in and near wetlands in the southeastern USA, Mexico, parts of the Caribbean, Central America, and northern South America.
Key Identifications:
- Fairly large white bird with a long reddish beak and long, red legs. Young birds have brown in their plumage and an orange beak and legs.
- Feeds on the ground, in and near wetlands. Eats frogs and other small creatures caught with its long bill.
- Makes a bulky stick nest and nests in colonies.
- A quiet bird. The White Ibis isn’t very vocal and only makes occasional nasal and guttural sounds. “Whaah, Whaah“.
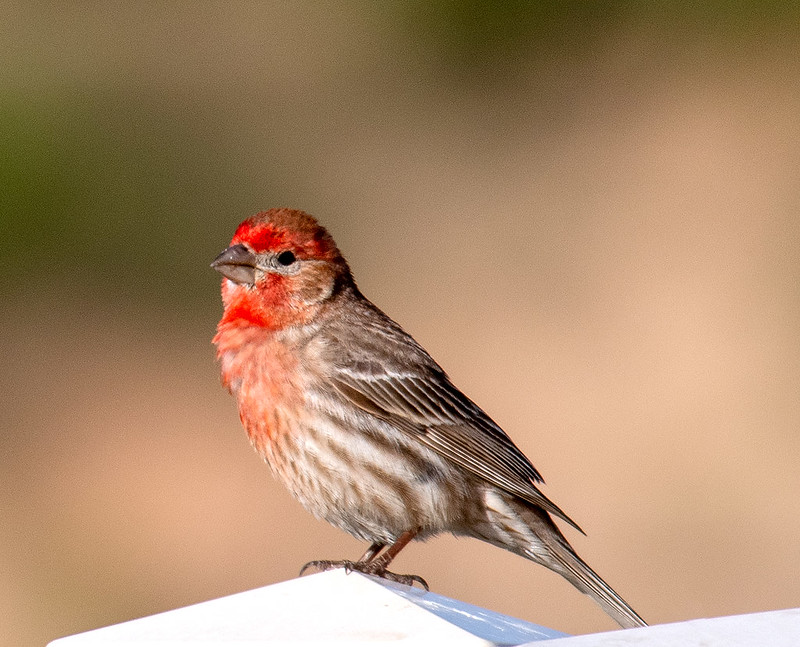
House Finch

Photograph © John Hansen
Scientific name: Haemorhous mexicanus
Length: 6 inches
Weight: .88 ounces
Wingspan: 10 inches
Song: “chip,chip,chiprididip,ZREEYachip”
House Finches are sparrow-sized birds with dark, rounded beaks and fairly long wings. Males are orange-red or rose-red on their head, throat and breast, and have some red on their rump. They also have brownish streaks on their back, flanks, and white belly.
Like the male, female House Finches have two white wing bars on long, gray-brown wings. However, they lack red and are mostly streaked dull brown-gray birds.
House Finches feed on seeds, buds, fruit, and flowers. They often visit feeders in Louisiana but also forage on the ground, and in bushes and trees.
We see these pretty birds in deserts and arid zones and in parks, farmland, urban areas, and other semi-open habitats.
The House Finch makes a soft cup nest built on a tree, building ledge or other spot with some overhanging cover. They often occur in small groups and live in southern Canada, most of the USA, Mexico, and Hawaii.
Key Identifications:
- Reddish or plain gray-brown, streaked, sparrow-like bird.
- Eats seeds, flowers, buds, and fruit. Can visit feeders but also forages on the ground and in bushes and trees.
- Makes a soft cup nest in trees, on building ledges, and other places.
- The House Finch often makes a soft, “fidip” call. Males also sing a warbling song from prominent, high perches. It sounds like, “chip,chip,chiprididip,ZREEYachip”.
Brown Thrasher
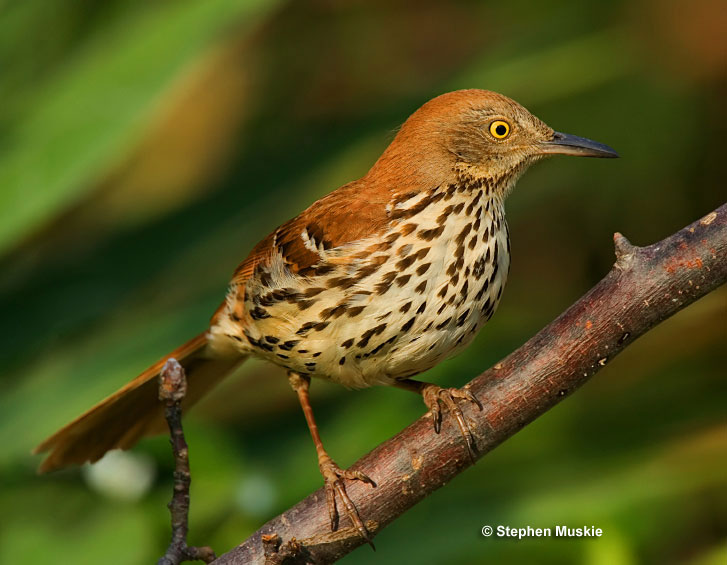

Scientific name: Toxostoma rufum
Length: 11.5 inches
Weight: 2.4 ounces
Wingspan: 13 inches
Song: “chree ree, chree ree, seerup seerup, cheer cheer, chrup chrup…”
The Brown Thrasher is a big slender bird with a long, rounded tail. Both sexes look alike and have bright reddish-brown upperparts, and dark brown streaks on pale buffy underparts.
They also have a grayish face, pale eyes, two narrow white wing bars, and a slender, slightly curved bill.
This species feeds on insects, small creatures, seeds, and fruit. It forages by using its beak to move leaves and soil to reveal food items and also forages in bushes and low trees.
The Brown Thrasher uses grass, sticks, and other bits of vegetation to make a bulky cup nest on or near the ground in a dense bush or low tree.
Brown Thrashers frequent second growth, brushy areas, and other similar habitats east of the Rocky Mountains in southern Canada and the USA.
Key Identifications:
- Large, slender, reddish-brown bird with a long tail and dark streaks on pale underparts.
- Forages on the ground and in low vegetation for insects, other small creatures, seeds, and fruit.
- Uses twigs and other materials to build a bulky cup nest in a low, dense vegetation, or the ground.
- Very vocal. Makes sharp smacking calls and sings a complex song of repeated double phrases that can include calls of other birds, “chree ree, chree ree, seerup seerup, cheer cheer, chrup chrup…”
Laughing Gull
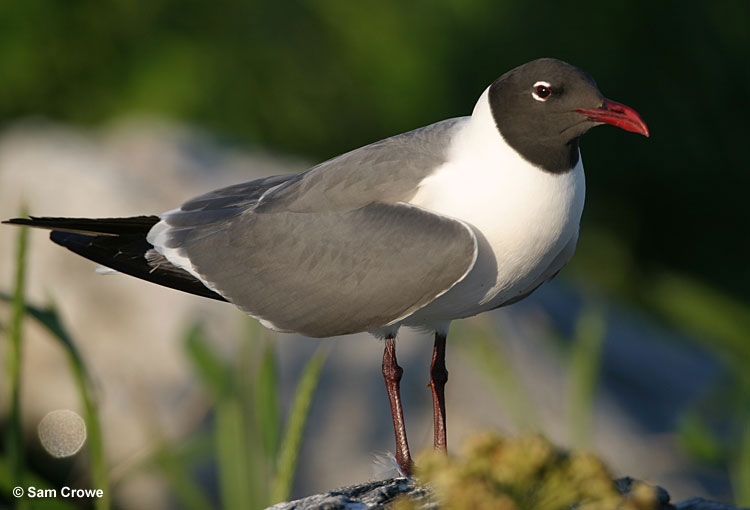

Scientific name: Leucophaeus atricilla
Length: 16.5 inches
Weight: 11 ounces
Wingspan: 40 inches
Song: “rih, ih, ih, ih, ih, ih, rah ha”
The Laughing Gull is a medium-sized gull with a dark gray back, mostly black wingtips, and two white marks above and below the eyes. In breeding plumage, male and female Laughing Gulls have thick, slightly hooked reddish beaks and black heads.
In winter, they have a dark bill with a reddish tip and only a bit of black on the head. Young birds are like winter adults but have more marks on their heads and darker wings.
Laughing Gulls feed on fish, carrion, berries, small creatures, and other items that they find on beaches and other coastal habitats.
They breed in colonies and make bulky, shallow cup nests out of sticks and other vegetation on coastal islands.
The Laughing Gull lives in coastal habitats of the eastern USA, Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean south to northern South America.
Key Identifications:
- Medium-sized gull with a dark gray back and wings, two white marks above and below the eyes, and, a black head (summer), or a white head with dark marks (winter).
- Feeds on fish, berries, and many other food items it finds in salt marshes and on beaches.
- Breeds in colonies on coastal islands and makes a bulky, shallow cup nest of sticks on the ground.
- The Laughing Gull is a vocal bird that makes brief laughing sounds, “rih, ih, ih, ih, ih, ih, rah ha”.
Common Grackle
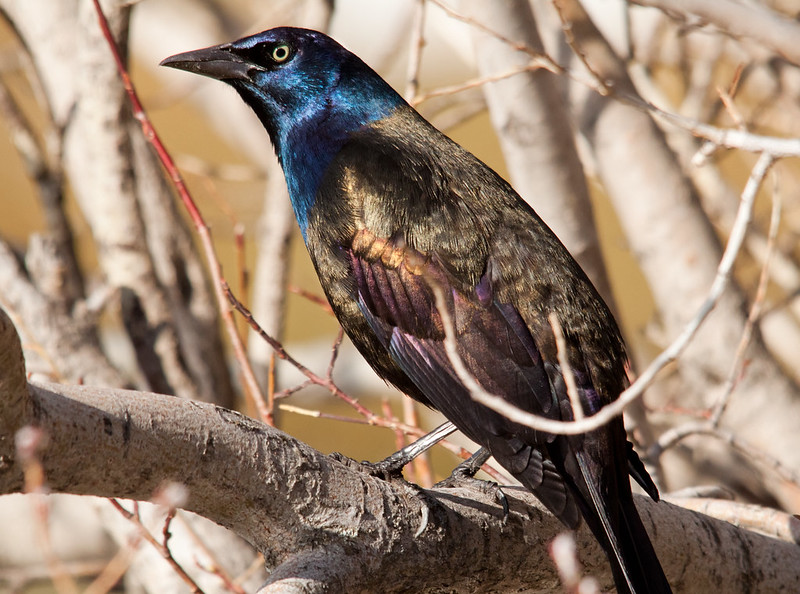

© Shawn McCready
Scientific name: Quiscalus quiscula
Length: 12.5 inches
Weight: 4 ounces
Wingspan: 17 inches
Song: “Sherink!”
The Common Grackle is a jay-sized, glossy black bird with pale eyes and a long, wedge-shaped tail. Depending on lighting, this bird shows metallic purple, blue, green, and bronze highlights.
Males and females look very similar, but females have shorter tails and less iridescence. Both sexes also have stout, black beaks, and strong, black legs and feet.
In flight, Common Grackles move up and down as they move through the air. They usually flock together and often forage in farm fields, on lawns, and in other open habitats. These omnivores feed on a variety of items, including insects, seeds, grain, small animals, garbage, and the eggs and nestlings of other birds.
Common Grackles build bulky stick nests, usually in conifers in woodlands, parks, near water, and urban areas. This species occasionally nests in odd places, including occupied nests of Great Blue Herons and Ospreys!
This species can form big flocks in the winter and lives in a variety of semi-open and open habitats in eastern Canada and the eastern USA.
Key Identifications:
- Fairly large, black bird with glossy purple, greenish, bronze, or dark blue highlights. It also has pale eyes and a long, wedge-shaped tail.
- Forages for insects, seeds, and other food on the ground in a variety of open habitats.
- Constructs a bulky cup nest in a conifer.
- Common Grackles are vocal birds. They frequently give raspy, metallic calls, “Sherink!”, and “kek” calls.
Double-crested Cormorant

Scientific name: Nannopterum auritum
Length: 33 inches
Weight: 3.7 pounds
Wingspan: 52 inches
Song: “groak”
The Double-crested Cormorant is a big, glossy black bird with a long, thick neck. Males and females look alike and also have a medium-length beak with a sharp, hooked tip, an orange throat patch, and a bit of orange on the face.
Double-crested Cormorants have a short, wispy crest, green eyes, broad tail, and big webbed feet. They use their long wings to flap and glide with direct flight between feeding and roosting areas.
This highly aquatic species feeds on fish. It catches its food by diving, swimming beneath the water and then snatching a fish with its beak. It eats the fish while perched above the water.
When it comes to fish, this species is not a picky eater; it has been documented eating more than 250 species.
The Double-crested Cormorant breeds in colonies and makes a messy stick nest in a tree on an island or above the water. We see this bird in parts of central and southern Canada, in much of the USA, and parts of Mexico and the Caribbean.
Key Identifications:
- Big, nearly goose-sized black bird with a long, thick neck, and a medium-length narrow beak with a small, hooked tip. It also has a rectangular, orange throat patch.
- Forages by floating and then diving beneath the water. Swims underwater to catch fish with its beak.
- Breeds in colonies and constructs a messy stick nest in trees on islands, or over water.
- Double-crested Cormorants aren’t very vocal. They make some low, guttural, pig-like sounds at their breeding colonies, “groak”.
Birds of Louisiana – Frequently Asked Questions
What kind of birds are in Louisiana?
Louisiana has White Ibis and other waterbirds, Swallow-tailed Kites, nesting Wilsons’ Plover, and many other species. Thousands of birds migrate through the state, Brown-headed Nuthatches live in the pine woodlands, and Great-crested Flycatchers call from neighborhood trees.
What is the most common bird in Louisiana?
The most common bird in Louisiana is the Northern Cardinal. According to the eBird platform and bird surveys, this species is seen more often than any other bird in the state.
What big birds are found in Louisiana?
Several big birds are found in Louisiana. A few of the biggest bird species in Louisiana are the Brown Pelican, Bald Eagle, and the tallest bird in North America, the Whooping Crane.
What birds are in the Bayou of Louisiana?
Birds that live in the Bayou of Louisiana include the Anhinga, Great Egret, various woodpeckers, and the beautiful Prothonotary Warbler.
Read next: Hawks in Louisiana | Ducks in Louisiana

