
The birds of Vermont lined up as 388 different magnificent species! Birds in Vermont include the beautiful Black-throated Blue Warbler, brilliant Scarlet Tanager, owls, and lots of other beautiful woodland species.
Vermont’s forests and farmlands are a haven for birds! There’s a lot to look at, how many birds were you able to identify?
This list shows the most common backyard and wild birds in Vermont. We hope it helps!
On this page
Most common birds of Vermont
According to eBird data from 2021 to 2023, these are the 25 most common birds of Vermont.
To help with identification, we also included information about their field marks and their behavior (remember that the species on the bottom of the list are common birds too!).
25 Most Common Vermont Birds
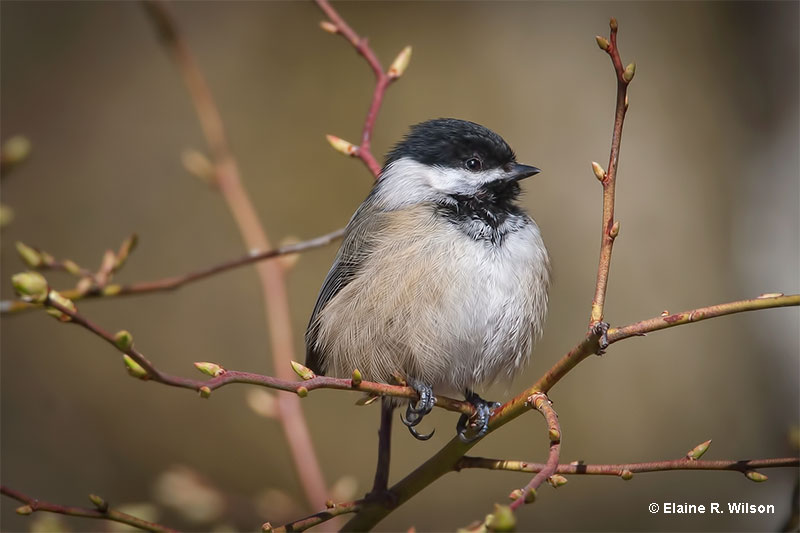
Black-capped Chickadee

Scientific name: Poecile atricapilla
Length: 5.25 inches
Weight: .39 ounces
Wingspan: 8 inches
Song: “see bee, see bee”
Black-capped Chickadees are small grayish birds with a black cap, black throat, and a stubby black beak. Both sexes look alike and have a white face, white edging to the feathers in their wings, and some buff on their underparts.
They are regular visitors to feeders but also forage on bark, twigs, and in foliage.
When foraging, they often hang upside down from twigs and usually occur in small flocks. These cute little birds feed on caterpillars, insects, spiders, seeds, and fruit.
This species makes a small, soft nest out of moss and deer hair. It builds its nest in tree cavities and can also use nest boxes.
Black-capped Chickadees live in a variety of wooded habitats and can also occur in gardens. They are year-round residents in parts of Alaska, Canada, and the northern USA south to Oregon, northern New Mexico, northern Ohio, and the Appalachian Mountains to North Carolina.
Key Identifications:
- Small, cute, grayish birds with a black cap, white face, and a black throat.
- Forages for insects, spiders, seeds, and fruit in wooded habitats. Also visits feeders.
- Nests in tree cavities and nest boxes.
- This little bird is quite vocal and often says its name, “chick-a-deedeedeedeedee”. They also make other chattering calls and sing a whistled song, “see bee, see bee”.
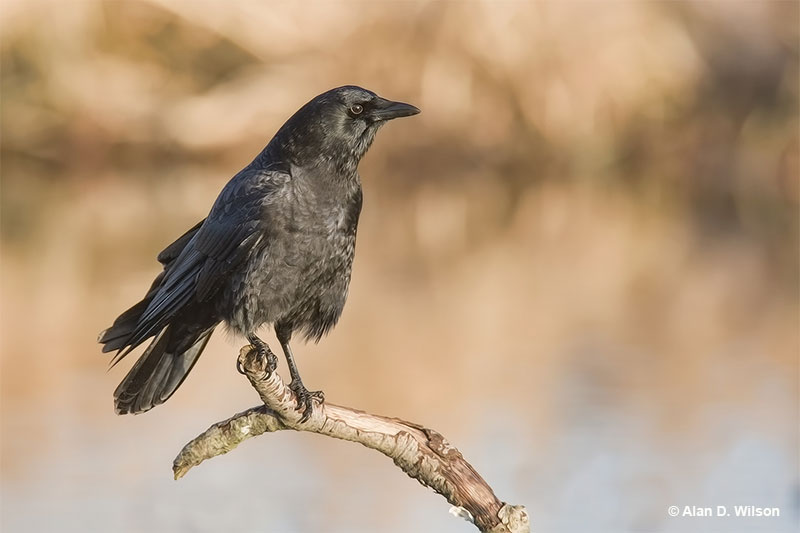
American Crow

© Alan D. Wilson
Scientific name: Corvus brachyrhynchos
Length: 17.5 inches
Weight: 1 pound
Wingspan: 39 inches
Song: “Caw! Caw!”
The American Crow is a big, all-black bird with a strong, stout bill. In certain lighting, it can have metallic purple and blue iridescence.
American Crows have a direct flight with strong, steady wing beats. Crows are very social and intelligent birds that are usually seen in flocks. They forage together on the ground or in trees and eat just about anything they can find.
Some of their more regular foods include carrion, fruit, nuts, seeds, insects, and small animals. Like most jays and crow species, they also eat the eggs and nestlings of other bird species.
This species builds bulky stick nests high in trees and lives in most habitats except for high mountains and arid zones.
The American Crow occurs in southern Alaska and much of Canada and the USA.
Key Identifications:
- Big, all black bird with long, broad wings and a broad tail.
- Forages for carrion, fruit, seeds, insects, and small animals.
- Builds a bulky stick nest high in a tree.
- American Crows are very vocal birds. They can make several calls but their most common one is, “Caw! Caw! Caw!”.
Blue Jay
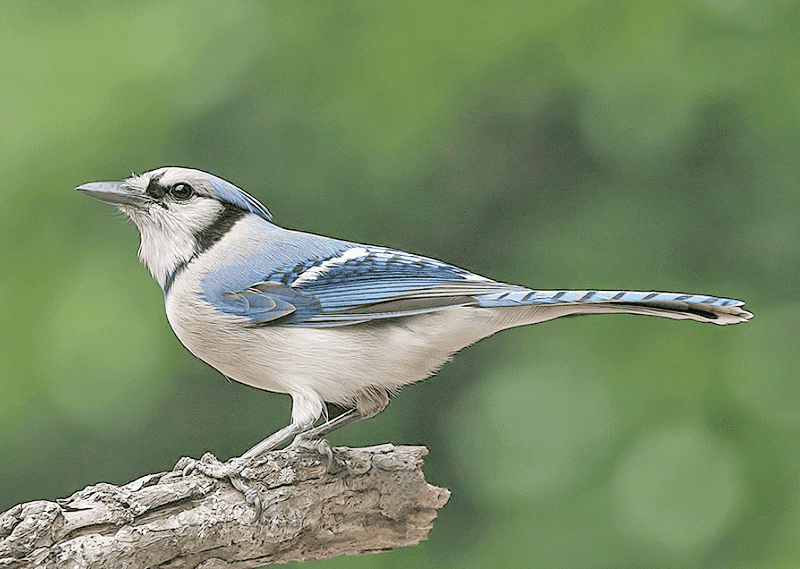
Photograph © Alan Wilson.
Scientific name: Cyanocitta cristata
Length: 11 inches
Weight: 3 ounces
Wingspan: 16 inches
Song: “Nyeah! Nyeah! Nyeah!”
The Blue Jay is a fairly large, crested bird with a straight black bill. Both sexes look alike and are blue above and gray and white below. They also have some small black lines on their faces and a narrow black necklace that goes up to the side of their face and crest.
Blue Jays also have some white markings and black barring on their wings and on their tail. Young birds look like adults but are duller blue.
They make messy cup nests at various heights in a variety of trees.
These social and intelligent birds feed on acorns, nuts, insects, and other small creatures. Like other members of the jay and crow family, they eat the eggs and nestlings of other birds.
The Blue Jay is a common bird of woodlands, forest, and towns east of the Rocky Mountains in the USA and central and southern Canada.
Key Identifications:
- Crested, fairly large bird with bright blue above and gray below.
- Feeds in trees and at feeders. Eats acorns, nuts, insects and many other food items.
- Makes a messy cup nest of sticks in a tree.
- Very vocal. In flight, Blue Jays often call as they swoop through the trees. They make a variety of sounds and mimic some other birds. Common calls include a nasal and complaining “Nyeah! Nyeah! Nyeah!” and various whistled calls.
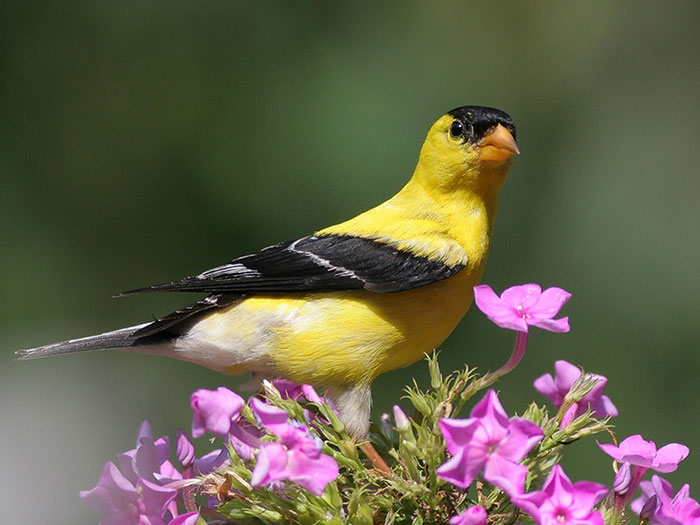
American Goldfinch

Scientific name: Carduelis tristis
Length: 5 inches
Weight: .46 ounces
Wingspan: 9 inches
Song: “swit sweet, sipsipsipchichisweetsweet”
The American Goldfinch is a small, sparrow-sized finch with a black and white, slightly forked tail, pale rump, and white undertail. In summer, males are bright lemon yellow with a small black cap, pale beak, and some white markings on long black wings.
Females and wintering birds have two pale wing bars and have plain gray, buff, and yellowish plumage. This species often occurs in small flocks and has bounding flight.
American Goldfinches feed on seeds. They forage by picking them from grass, thistle, other low plants, Alders, and other trees. Goldfinches are also frequent visitors to bird feeders.
The American Goldfinch uses plant matter and other soft materials to build a small, tightly woven cup nest high in a shrub or a low tree.
American Goldfinches are summer residents in southern Canada, California, and the northern half of the USA, and winter in most of the USA and parts of Mexico.
Key Identifications:
- Small, bright yellow finch with a black cap, wings and tail (summer male), female and winter males are plain brown, buff, and yellowish birds with two pale wing bars.
- Feeds on seeds in low plants, trees, and at feeders.
- Makes a tightly woven cup nest high in a shrub or low tree.
- Often gives a “per chickory” call in flight and sings a short, trilled song, “swit sweet, sipsipsipchichisweetsweet”.
American Robin
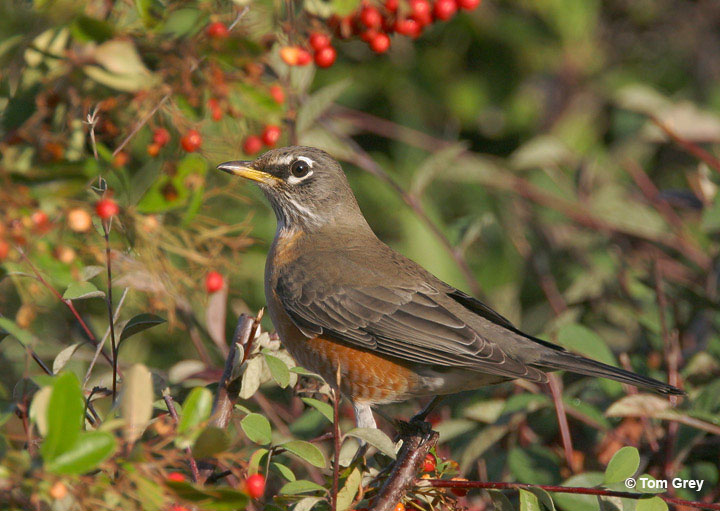

Scientific name: Turdus migratorius
Length: 10 inches
Weight: 2.7 ounces
Wingspan: 17 inches
Song: “cheery, cheery, cheery, cheery, cheer, cheer”
The American Robin is a familiar and common thrush that is dark gray above and brick red below. It also has an orange-yellow bill, a blackish head with white markings around the eyes and on the throat, and a white belly.
Both sexes of this thrush species are similar, but males are darker above and more reddish on the underparts. Young American Robins have more white marks on their faces and spotting on orange underparts.
In flight, this common thrush in Vermont also shows white corners in its outer tail feathers.
American Robins forage on the ground for worms, insects, snails, and other small creatures. In winter, these common birds flock together and perch in trees and bushes to eat berries and fruit.
The American Robin makes a cup nest in trees and lives in parks, woodlands, towns, and many other habitats. These birds reside in Alaska, most of Canada, the USA and in Mexico.
Key Identifications:
- Fair-sized songbird that is dark gray above, and brick red and white below.
- Forages for worms and bugs on lawns and other open grassy areas, also flocks together to feed on fruiting trees in the winter.
- Makes a cup nest in trees.
- The American Robin is quite vocal and makes a loud, sharp, “yenk!” call and quieter “check,check,check” calls. It also has a lovely cheerful song of caroled phrases, “cheery, cheery, cheery, cheery, cheer, cheer”.
Northern Cardinal
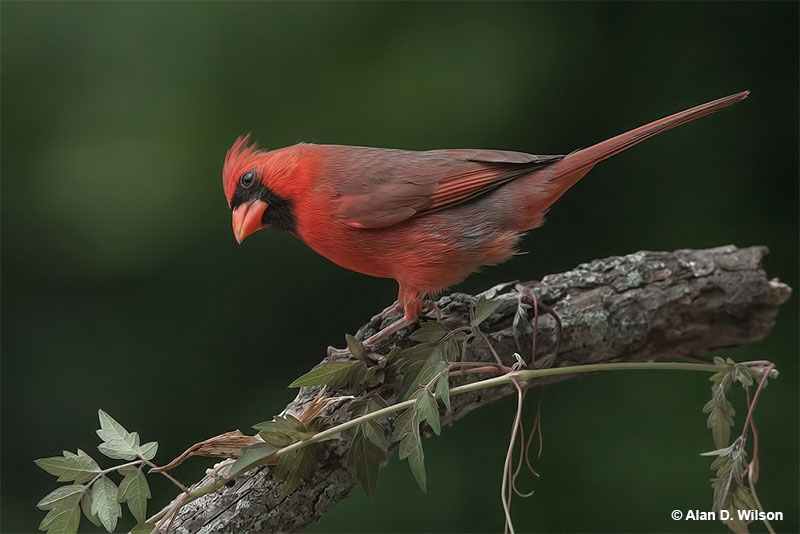

Scientific name: Cardinalis cardinalis
Length: 8.75 inches
Weight: 1.6 ounces
Wingspan: 12 inches
Song: “pichew-pichew-pichew, chew,chew,chew,chew,chew”
Northern Cardinals are medium-sized songbirds with a perky crest and big orange-red beak. Males are bright red with a black throat and face, and have dusky red on their back, wings, and tail.
Female Northern Cardinals are grayish-brown and buff with some black on their face and throat. They also have red highlights on their crest, wings, and long, rounded tail.
This species has short, rounded wings and seems to bounce up and down as they move through the air. In flight, Northern Cardinals also make sharp chip notes.
It eats seeds, insects, and some fruit and is a regular visitor to bird feeders. They forage on and near the ground, but males sing from a prominent perch.
This beautiful bird occurs in pairs and nests in bushes and low trees. It is common in the eastern and southwestern USA, southern Ontario, and in Mexico.
Key Identifications:
- Crested bird with a conical orange-red beak and a black face. Males are red, females are grayish-brown and buff.
- Forages for seeds and insects on and near the ground.
- Makes a cup-shaped nest in bushes and low trees.
- Sings a clear, whistled song of repeated notes. They can sound like “cheer, cheer, chew, chew, chew, chew” or a quick “birdee,birdee,birdee,birdee,birdee“. They also make loud, sharp chip notes.
White-breasted Nuthatch
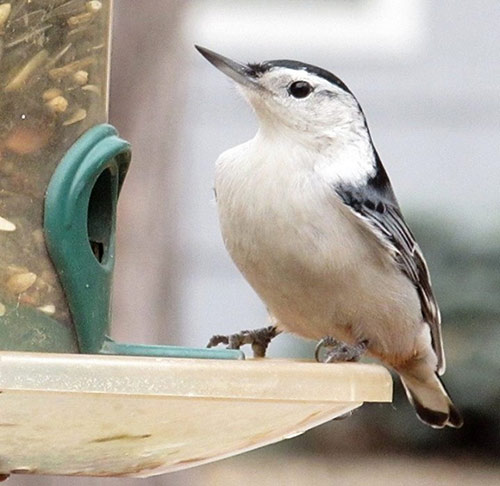

Scientific name: Sitta carolinensis
Length: 5.75 inches
Weight: .74 ounces
Wingspan: 11 inches
Song: “wehn wehn wehn wehn wehn wehn wehn wehn”
The White-breasted Nuthatch is a sparrow-sized bird with a longish, sharp, slightly upturned beak and a short black and white tail. It also has long wings, is mostly blue-gray above, and white and gray below, with some chestnut on its belly and undertail.
Both sexes look similar and have a white face, but males have a black cap and nape. Females have gray on their head and nape.
This small bird forages for insects, nuts, and seeds by creeping along branches and going down trunks, head-first. It uses its beak to pick food items from bark and also visits feeders.
The White-breasted Nuthatch makes a cup nest out of grass and soft bark inside a tree cavity or nest box.
White-breasted Nuthatches live in various wooded habitats in parts of southern Canada, most of the USA, and mountains in Mexico. They are frequent visitors to gardens near woodlands.
Key Identifications:
- Sparrow-sized, short-tailed songbird that is blue-gray above, mostly white below, and has a longish, slightly upturned beak.
- Creeps on branches and down tree trunks for insects, nuts, and seeds. Also visits feeders.
- Uses grass and soft bark to make a cup nest in a tree cavity or nest box.
- Quite vocal and makes nasal calls “yank yank”, and sings a nasal, laughter-like song, “wehn wehn wehn wehn wehn wehn wehn wehn”.
Song Sparrow
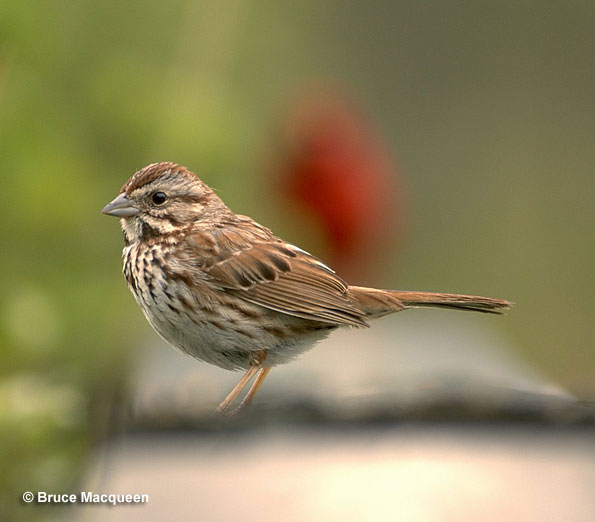

Scientific name: Melospiza melodia
Length: 6.25 inches
Weight: .7 ounces
Wingspan: 8.25 inches
Song: “seet serate sitsziziziziziziziz seet”
The Song Sparrow is a small, gray and brown, streaked songbird with a thick dark mark on each side of its white throat. Males and females look the same and have white underparts with a dark brown mark on their breast and dark brown streaks on their breast and sides.
Most Song Sparrows also have two narrow wing bars and show a rounded tail when fluttering between bushes.
This species feeds on insects, seeds, and small fruits. Pairs forage by picking up food items on and near the ground. They are also frequent visitors to bird feeders.
Song Sparrows use grass, stems, hair, and other materials to make a cup nest placed on or near the ground. They nest in dense vegetation, shrubbery, or low trees, often near water.
This species uses a wide variety of brushy habitats in open and wooded situations in southern Alaska, most of Canada, and all of the USA.
Key Identifications:
- Small brown, streaked sparrow with a dark mark on its breast.
- Forages on and near the ground for seeds and insects in brushy habitats.
- Builds a cup nest on or near the ground in a shrub or low tree.
- Makes high-pitched “tink”, chirping calls, and has a cheerful song with a trill, “seet serate sitsziziziziziziziz seet”.
Tufted Titmouse
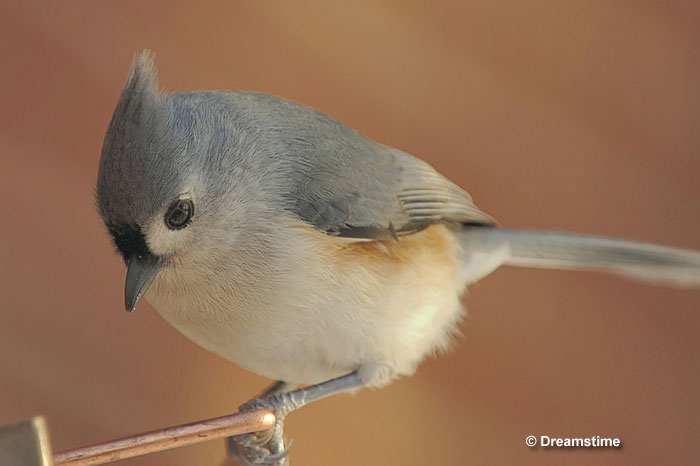

Scientific name: Baeolophus bicolor
Length: 6.5 inches
Weight: .75 ounces
Wingspan: 9.75 inches
Song: “peter peter peter”
The Tufted Titmouse is a small, crested, blue-gray bird with a white face. Males and females look the same and have a small black mark above their stubby black beak. They also have pale underparts with peach-orange flanks.
These cute little birds occur in small groups that forage for insects and seeds in parks and woodlands. They move through the trees and use their bills to pick food from leaves, bark, and branches. Tufted Titmouse are also regular visitors to bird feeders.
These small birds nest in woodpecker holes and other cavities in dead trees, and can also use nest boxes.
We find the Tufted Titmouse in hardwood forests and forested urban areas. They are often heard before they are seen and flock with other small birds. When they see a predator, they are some of the first birds to harass it.
The Tufted Titmouse occurs in the eastern USA and some parts of southeastern Canada.
Key Identifications:
- Small, crested blue-gray bird with pale underparts and a white face.
- Feeds on seeds and insects and visits feeders.
- Nests in tree cavities and nest boxes.
- The Tufted Titmouse is a very vocal bird. It gives constant whistled calls over and over, “peter peter peter“.
Mourning Dove
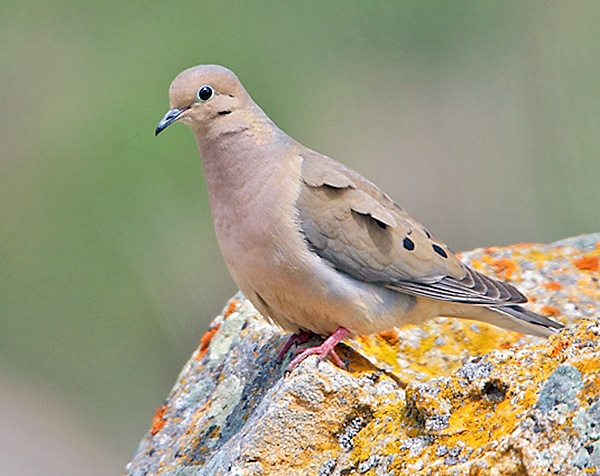

Photograph © Greg Lavaty.
Scientific name: Zenaida macroura
Length: 12 inches
Weight: 4.2 ounces
Wingspan: 18 inches
Song: “hooOOA, hoo, hoo, hoo”
Mourning Doves are medium-sized, grayish-brown doves with long tails. They have small black spots on their wings and a small head with a slender, dark beak.
Males and females also have narrow gray eyerings, a black mark on the face, and pale iridescent gold on the sides of their necks. They look alike except for males having more gray on the head and neck, and more iridescence.
This dove has fairly long wings and swift, direct flight. When flying, it shows black and white on its tail.
The Mourning Dove occurs in woodlands, gardens, on farms, and in urban areas. This common feeder visitor eats seeds and grains. It also forages in open situations, picking food from the ground.
This pleasant dove species can visit a feeder on its own or forage in small flocks. It builds an unkempt stick nest in bushes and trees and is very common throughout the USA, southern Canada, and Mexico.
Key Identifications:
- Plain brown and gray dove with a long, pointed tail.
- Feeds on seeds at feeders and on the ground in open areas.
- Makes a small, messy nest of sticks in trees.
- Sings a sad and owl-like “hooOOA, hoo, hoo, hoo”.
Downy Woodpecker
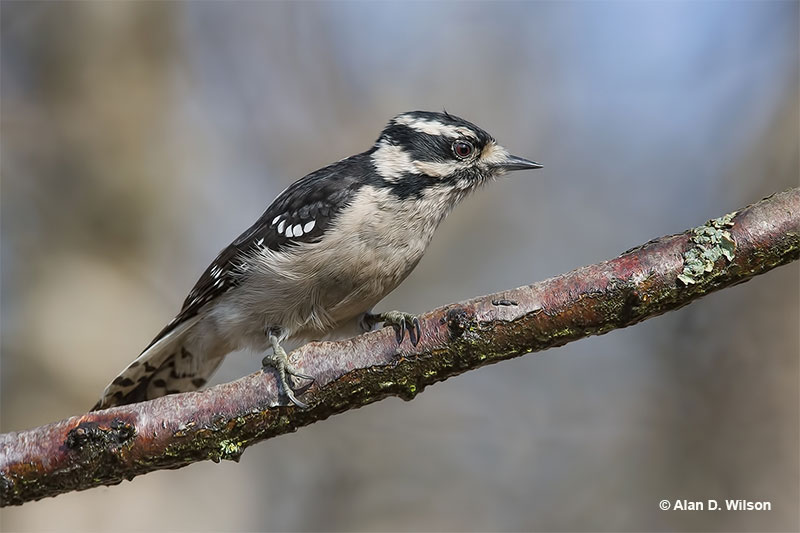

Scientific name: Dryobates pubescens
Length: 6.75 inches
Weight: .95 ounces
Wingspan: 12 inches
Song: “Pik! Ch,ch,ch,ch,ch,ch,ch!”
The Downy Woodpecker is a small black and white woodpecker with a short, black beak. They are patterned black and white above and have white backs and white underparts. Both sexes look alike, but males have a small, bright red patch on the top back part of their head.
Downy Woodpeckers also have a few small black marks in their white outer tail feathers, and a small white tuft at the base of their beak.
This woodpecker eats insects, other small creatures, seeds, and small fruits. It pecks into live and dead wood and often forages on smaller branches and twigs. These friendly little woodpeckers are also common feeder birds.
They nest in tree cavities and live in gardens and a wide variety of woodlands. We see Downy Woodpeckers in much of Canada and the USA, but not in arid habitats.
Key Identifications:
- Smallest woodpecker in North America. Mostly black and white with a short, black beak.
- Forages on trees, in bushes, and at feeders for insects, seeds, and suet.
- Nests in tree cavities.
- The Downy Woodpecker makes sharp “pik!” calls and also has a trilled call, “Ch,ch,ch,ch,ch,ch,ch!“.
Dark-eyed Junco
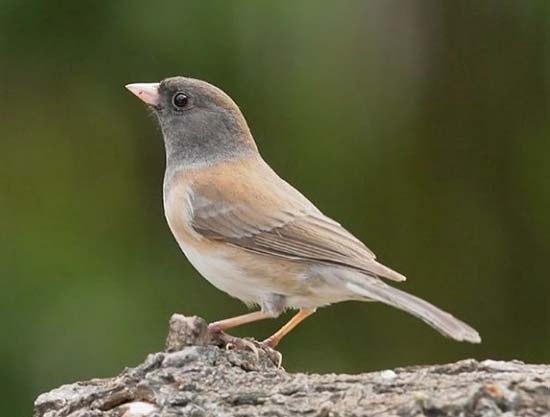

Scientific name: Junco hyemalis
Length: 6.25 inches
Weight: .67 ounces
Wingspan: 9.25 inches
Song: “sipsipsipsipsipsipsip”
Dark-eyed Juncos are sparrow-like birds with pale conical bills and dark eyes. This small bird has variable plumage, with most being slate gray or gray and brown with white on their bellies, and white under their tails.
Other plumages include birds with dark masks and faint white wing bars, juncos with pale gray hoods and pinkish sides, and birds with blackish hoods and chestnut sides.
In flight, all Dark-eyed Juncos show extensive white in their longish tails.
This species feeds on seeds, insects, and some fruit and grain. Juncos forage on the ground in wooded areas, parks, and other habitats. They also feed on fallen seed beneath feeders.
They build cup nests on the ground under fallen logs, in roots, and in other hidden spots. After breeding, juncos form flocks that forage together in similar wooded and semi-open habitats.
Dark-eyed Juncos are common birds in Canada, the USA, and parts of Mexico.
Key Identifications:
- Sparrow-like gray and brown bird with dark eyes, a pale beak, and white in the tail.
- Forages for seeds and insects on the ground, can feed on seeds at and beneath feeders.
- Builds a cup-shaped nest on the ground in tree roots, under logs, and other hidden places.
- This species often makes a sharp, high-pitched chip note, “pik!”. On breeding grounds, males sing a short, plain trill, “sipsipsipsipsipsipsip”.
Red-winged Blackbird
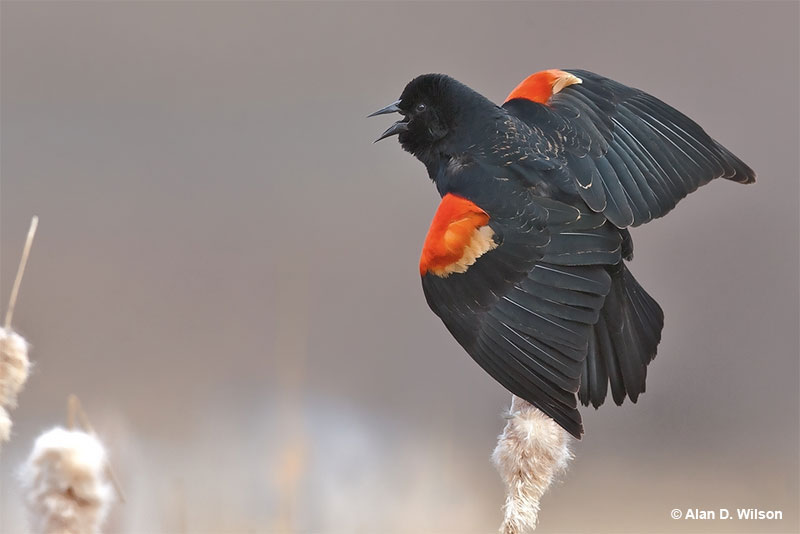

Scientific name: Agelaius phoeniceus
Length: 8.75 inches
Weight: 1.8 ounces
Wingspan: 13 inches
Song: “kan-keree!”
The Red-winged Blackbird is a medium-sized blackbird species with a sharp black bill. Males also have a scarlet patch with a pale yellow border on the shoulder of each wing.
Female Red-winged Blackbirds are dark, heavily streaked, brownish-gray birds with an orange-buff eyebrow and throat.
Red-winged Blackbirds often flock together and can form very large groups in the winter. They feed on seeds, grain, and insects found on lawns, in marshes, farm fields, and other open habitats.
This species builds a cup nest made of leaves and dead stems in a bush or other low vegetation in a marsh, park, or brushy field.
Red-winged Blackbirds are very common birds that live in all sorts of open habitats. We see them in parks, farming areas, and marshes in much of Canada, the USA, Mexico, and parts of the Central America.
Key Identifications:
- Males are medium-sized blackbirds with a bright red patch on their wings. Females are heavily streaked, have a sharp black beak, and buff on the head.
- Feeds on seeds, grain, and insects on the ground in many open habitats.
- Builds a cup nest in a bush or other low vegetation.
- Red-winged Blackbirds often call. Males sing a loud, “kan-keree!” and both sexes also make “check!” calls and a high-pitched whistle-like sound.
Hairy Woodpecker
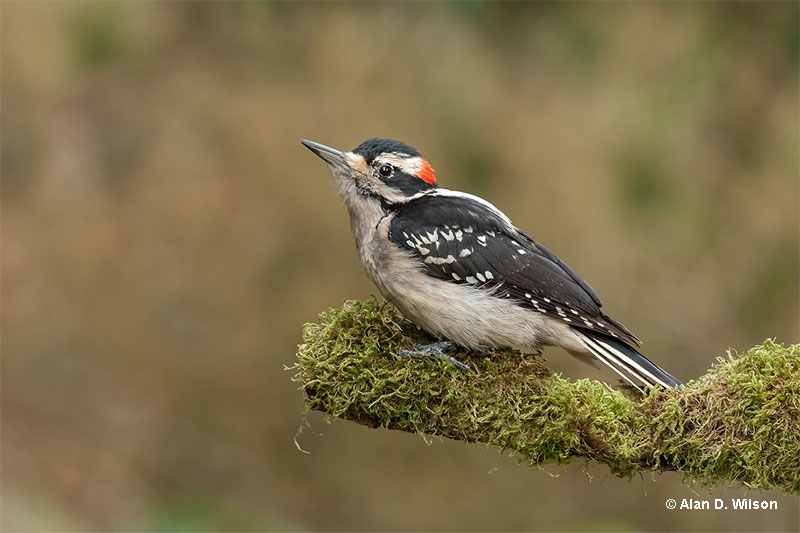

© Alan D. Wilson
Scientific name: Dryobates villosus
Length: 9.25 inches
Weight: 2.3 ounces
Wingspan: 15 inches
Song: “Qquechichichichichichicchichic!”
Hairy Woodpeckers are medium-sized, black and white woodpeckers with long, straight beaks. They have a white patch on their back and a black and white tail with unmarked, white outer tail feathers.
Both sexes look very similar, but males have a small, bright red spot on the back of their head. Young birds have a dull red patch on top of their heads.
This woodpecker species feeds on insects, other small creatures, and a variety of seeds and fruit. They forage by pecking into bark and picking berries and other fruit from branches. In areas with big, mature trees, Hairy Woodpeckers are also regular visitors to bird feeders.
The Hairy Woodpecker nests in tree cavities. This species lives in parks and woodlands with mature trees in Alaska, much of Canada, and in most of the USA, including Vermont.
They are absent from southern Florida and arid parts of the American Southwest.
Key Identifications:
- Medium-sized, black and white woodpecker with a long straight beak and unmarked, white outer tail feathers.
- Picks insects and fruit from bark of big trees, also eats seeds at feeders.
- Nests in tree cavities.
- Often calls and gives a sharp and explosive, “Peek!” and a longer rattle, “Qquechichichichichichicchichic!”.
Canada Goose
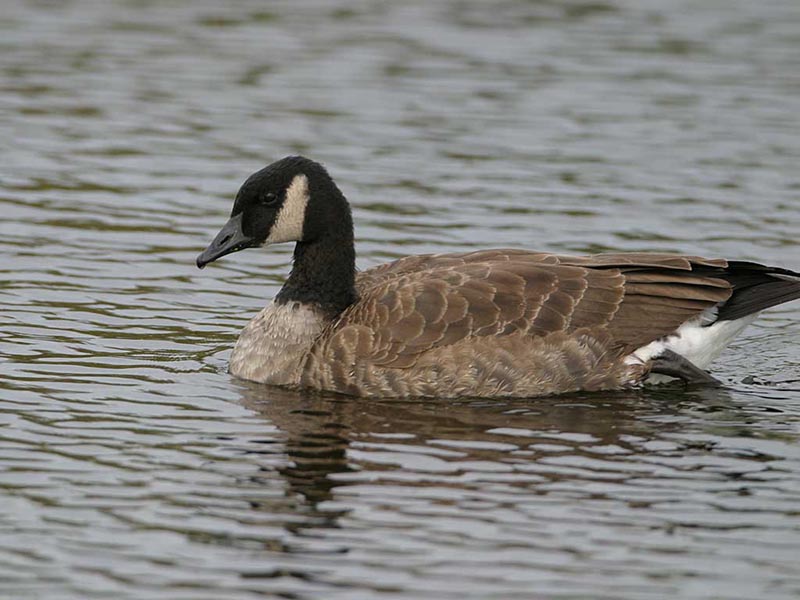

Scientific name: Branta canadensis
Length: 35 – 45.2 inches
Weight: 5.29 – 19.8 pounds
Wingspan: 50 – 67 inches
Song: “uurrRUNK! uurrRUNK!”
The Canada Goose is a large, grayish-brown bird with a long black neck, and black head with a white throat and cheeks. Males and females look alike and have pale barring, a white belly and undertail, and a short black and white tail.
They have strong, direct flight and make deep flaps with long, broad wings.
Canada Geese feed on grass, sedges, and other vegetation, grain, and berries. They forage by walking along and grazing, or picking food from the ground and bushes. This species also feeds by dipping its head below the surface of shallow water.
This large goose uses grass and other plants to make a large, shallow cup nest on a small mound or other elevated spots near water.
The Canada Goose prefers open grassy areas and farm fields near water where it can feed and see predators before they get too close.
They live in Alaska, most of Canada, and most of the USA, being one of the most common birds of Vermont.
Key Identifications:
- Big, gray-brown goose with a long black neck, and black and white head.
- Grazes vegetation and forages for berries in wide open, grassy habitats near water like golf courses, parks, and airports.
- Makes a shallow, open cup nest on an elevated spot next to water.
- Vocal and often makes honking calls, “uurrRUNK! uurrRUNK!”.
Common Raven
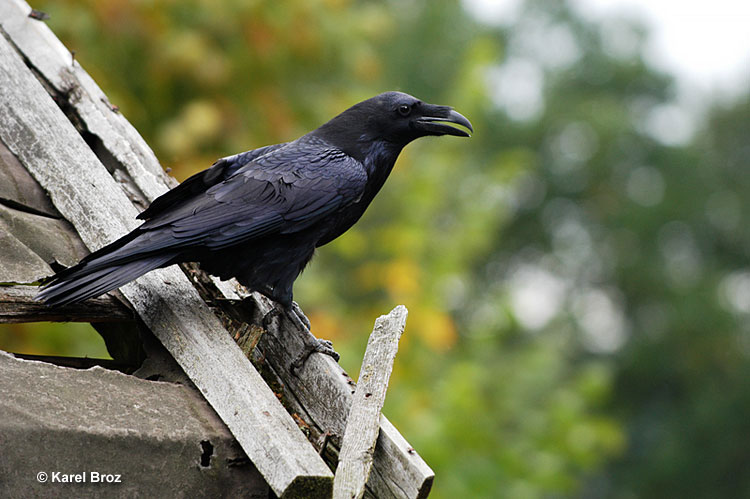

Scientific name: Corvus corax
Length: 24 inches
Weight: 2.6 pounds
Wingspan: 53 inches
Song: “Grauk Grauk Grauk Grauk!”
The Common Raven is a big, black crow-like bird with long, broad wings and a broad, wedge-shaped tail.
Both sexes look alike and have feathers extending onto the top part of their strong, stout beaks.
This bird is often seen in soaring flight or in direct flight, where it gives a few strong flaps between glides.
Common Ravens are omnivores that feed on carrion, small animals, nesting birds, and various other food items. They forage by flying above roads and other places and are always on the lookout for feeding opportunities.
This big Corvid makes a big, bulky nest out of sticks and lines the shallow cup with mud, wool, and other items. It builds its nest on a cliff, tree, bridge, or other structure.
The Common Raven lives in wilderness areas from the Arctic to parts of the northeastern USA and the western USA. In some places, it lives in urban areas. Common Ravens are common birds in Vermont.
Key Identifications:
- Huge, black, crow-like bird with a strong, stout beak and a wedge-shaped tail.
- An omnivore that feeds on small animals, carrion, and other food items.
- Makes a big bulky stick nest in trees, on cliffs, and on human-made structures.
- Common Ravens are vocal birds. One of their most common calls is a load and croaking, “Grauk Grauk Grauk Grauk!”.
Red-breasted Nuthatch
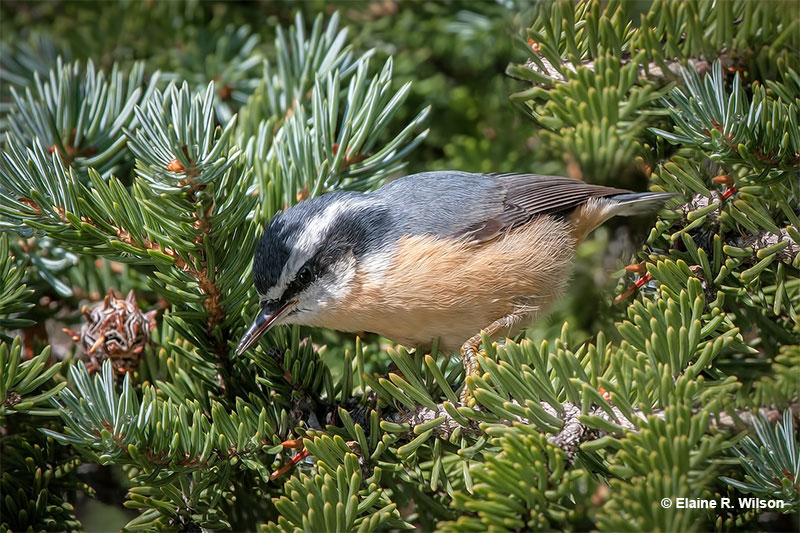

© Elaine R. Wilson
Scientific name: Sitta canadensis
Length: 4.5 inches
Weight: .35 ounces
Wingspan: 8.5 inches
Song: “yeank, yeank, yeank”
The Red-breasted Nuthatch is a small, warbler-sized bird with a dark gray, straight or slightly upturned beak, gray upperparts, and reddish-orange underparts. It also has a black cap, a white face with a narrow black mask, and black and white in its short tail.
Males and females are similar, except that females are paler and have a gray cap.
Red-breasted Nuthatches eat insects during the summer and conifer seeds in the winter. These small, animated birds forage by creeping down coniferous tree trunks and on branches. They use their bills to probe bark and pick out insects and seeds.
This species excavates a tree cavity and makes an open nest of bark and other vegetation.
The Red-breasted Nuthatch lives in coniferous and mixed forests in southern Alaska, Canada, and the western and northern USA. They also breed in the Appalachians and can be seen in most of the USA in winter.
Key Identifications:
- Small, short-tailed bird with a narrow white eyebrow, black mask, gray upperparts, and reddish-orange underparts.
- Creeps along tree trunks and branches to forage for insects and conifer seeds.
- Nests in tree cavities.
- The distinctive nasal call of the Red-breasted Nuthatch, “yeank, yeank, yeank”, is a good way to find this bird.
Eastern Phoebe
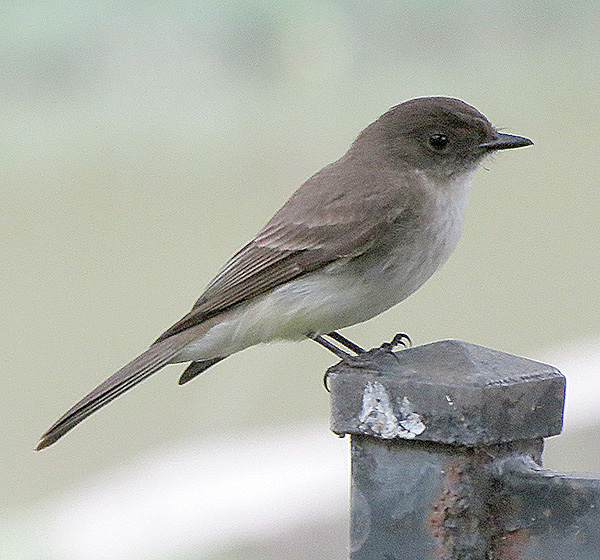

Photograph © Sam Crowe.
Scientific name: Sayornis phoebe
Length: 7 inches
Weight: .7 ounces
Wingspan: 10.5 inches
Song: “see-BEE! See BIDIT”
The Eastern Phoebe is a small to medium-sized, plain flycatcher that is dark, brownish gray above, and white below. It also has gray on its breast and a long, blackish tail that constantly wags up and down. This bird also has a blackish head and some pale edging on long, dark wings.
This flycatcher uses its slender beak to snap up insects. It catches them by flying from a perch and snatching them in flight, from foliage while hovering and from the ground.
We usually see Eastern Phoebes on their own, sitting on low or medium-height perches. They make cup nests of mud, moss, and leaves on rocky outcrops, and under bridges and other structures.
This species breeds in woodlands and parks in Canada and the eastern USA, and winters in similar habitats the southeastern USA and Mexico.
Key Identifications:
- Plain, mid-sized flycatcher that is dark brownish-gray above and pale below with some gray on the breast.
- Perches low to mid-height in woodlands and flies out to catch insects. It also feeds on berries in winter.
- Makes a cup nest of mud and vegetation on structures and rocky outcrops.
- Sings a song that sounds like its name, “see-BEE! See BIDIT”.
Red-eyed Vireo
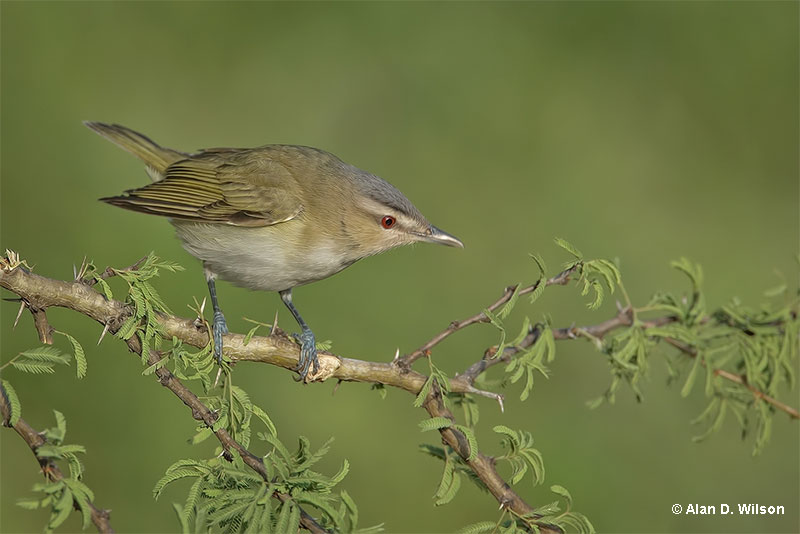

Scientific name: Vireo olivaceus
Length: 6 inches
Weight: .6 ounces
Wingspan: 10 inches
Song: “See me? Up here! Here I am…See me?”
The Red-eyed Vireo is a small, pale bird that is olive above and white below. Both sexes are similar and have a gray crown with a narrow black border separating it from its white eyebrow.
It also has a dark line through its reddish eyes, a grayish beak with a small hooked tip, and some pale yellow under its tail.
Red-eyed Vireos feed on caterpillars and insects. They forage by steadily moving through leafy vegetation and then picking food items from leaves and twigs. They also eat berries in the fall and on their wintering grounds.
This species builds a small cup nest out of lichen, small twigs, and other plant matter. The female usually constructs the nest high in a deciduous tree.
The Red-eyed Vireo breeds in forest habitats in Canada, and the northern and eastern USA, and winters in tropical forests habitats in the Amazon basin.
Key Identifications:
- Small, pale bird with a gray crown that is olive above, white below, and has a dark line through its reddish eyes.
- Makes a small cup nest our of twigs, lichen, and other plant matter high in a tree.
- The male Red-eyed Vireo constantly sings, “See me? Up here! Here I am…See me?”. When alarmed, Red-eyed Vireos also make harsh, rasping calls.
Gray Catbird
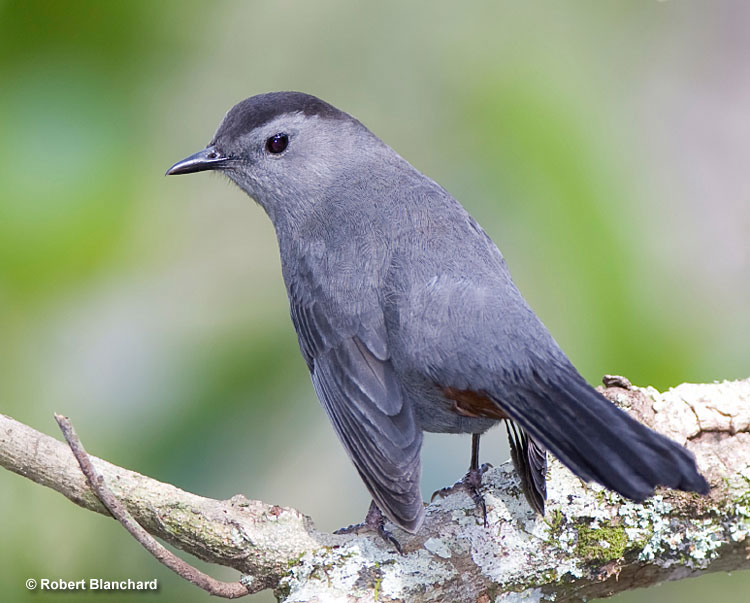

Scientific name: Dumatella carolinensis
Length: 8.5 inches
Weight: 1.3 ounces
Wingspan: 11 inches
Song: “rheah!”
The Gray Catbird is a slender, gray songbird with a black cap and chestnut under its tail. Both sexes look alike and have beady, black eyes on a gray face, a longish tail, and a smallish, black beak.
This reclusive bird feeds on insects and berries in thickets and second growth. It forages by moving through dense vegetation and picking food items from leaves and twigs.
Gray Catbirds make bulky, open cup nests constructed with grass, strips of vegetation, and hair. They build their nests in shrubs, bushes, and small trees.
The Gray Catbird is often heard before it is seen and loves to skulk in low, thick vegetation.
This migrant species spends summers in southern Canada, and in much of the eastern and northern USA. In fall, it migrates to coastal areas in the eastern and southern USA, and Florida south to northern South America.
Key Identifications:
- Small to medium-sized, slender gray bird with a black cap and chestnut under the tail.
- Feeds on insects and berries in low, dense vegetation.
- Builds a bulky cup nest in small trees and bushes.
- The Gray Catbird is quite vocal and often makes a cat-like mewing call, “rheah!”. It also has a melodious, complex song made of jumbled, chattering sounds and phrases.
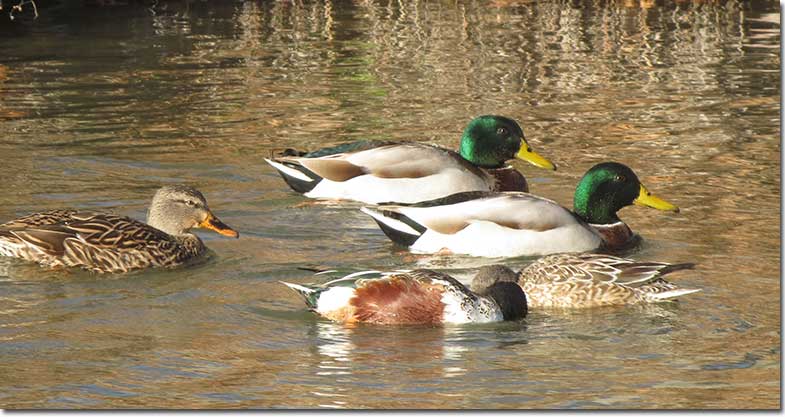
Mallard
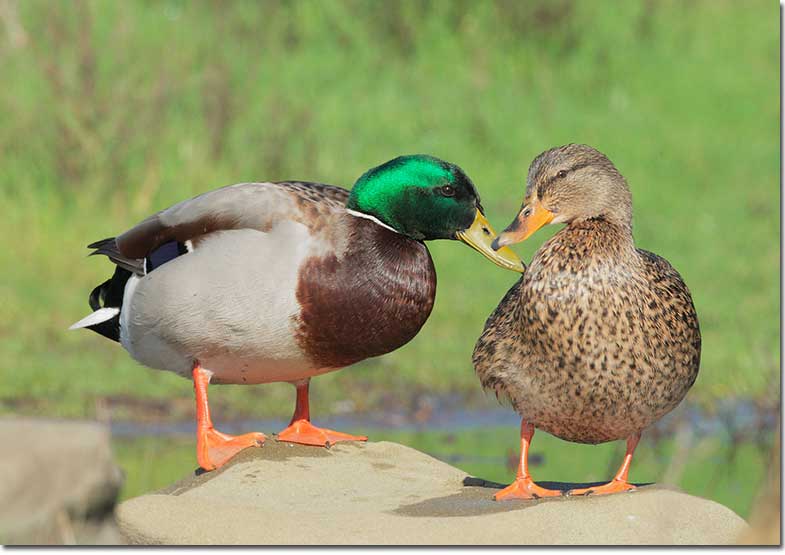

Mallard pair (Male and female)
Scientific name: Anas platyrhynchos
Length: 23 inches
Weight: 2.4 pounds
Wingspan: 35 inches
Song: “quack, quack”
The Mallard is a fairly large, familiar duck. The male has a metallic green head, yellow bill, narrow white ring around the neck, and chestnut breast. The rest of the bird is pale gray with pale brown and black on its back and around his tail.
Female Mallards are mottled brown and buff with a dark crown and line through the eyes, and have a dark gray and orange beak.
In flight, both sexes show a green-blue wing patch bordered with white.
Mallards eat a variety of items, including insect larvae, snails, other small aquatic creatures, acorns, seeds, and grain. They forage by filtering and picking up food items in and near shallow water, and in farm fields.
This duck species makes a shallow nest with sticks and lined with down feathers. It builds its nest on the ground, hidden in grass or under a bush.
The Mallard lives in ponds, marshes, and many wetland habitats in Canada, USA, and Eurasia.
Key Identifications:
- Feeds on insect larvae, grain, seeds, and other items picked up with its bill in and near shallow water.
- Makes a shallow stick nest hidden in grass or under a bush.
- The female Mallard makes the classic “quack, quack” duck sound. Males make similar but softer sounds and a whistling call.
European Starling

Photograph © Greg Lavaty.
Scientific name: Sturnus vulgaris
Length: 8.5 inches
Weight: 2.9 ounces
Wingspan: 16 inches
Song: “tiktiktitZHREEree..tiktiktik..ZHREE”
European Starlings are plump, short-tailed birds with long sharp beaks and longish, pointed wings. In summer, they have yellow beaks, glossy black plumage with purple and green highlights, and some small white spots.
Young starlings are shaped like adults but are grayish birds with a dark beak and a pale throat.
This species feeds on a variety of insects, fruit, and seeds. They can dominate bird feeders and are common species in urban areas, parks, farmlands, and other open habitats.
European Starling builds a soft cup nest in a tree cavity, nest box, or suitable cavity in other structures.
European Starlings flock with each other and blackbird species, especially during the winter. They live across a large part of Canada and the USA.
Key Identifications:
- Rotund, short-tailed bird with a long, sharp beak, and pointed wings. Glossy black with some spotting in the summer and blackish with heavy white spotting and streaking in the winter.
- Feeds on seeds, fruit, and insects. Visits feeders and forages on the ground in flocks.
- Builds a soft cup nest in nest boxes and other cavities.
- The European Starling makes a wide variety of mechanical and whistled sounds. They also mimic other birds and sounds in their environment. They sing long, jumbled mechanical-sounding songs, “tiktiktitZHREEree..tiktiktik..ZHREE”.
Common Yellowthroat
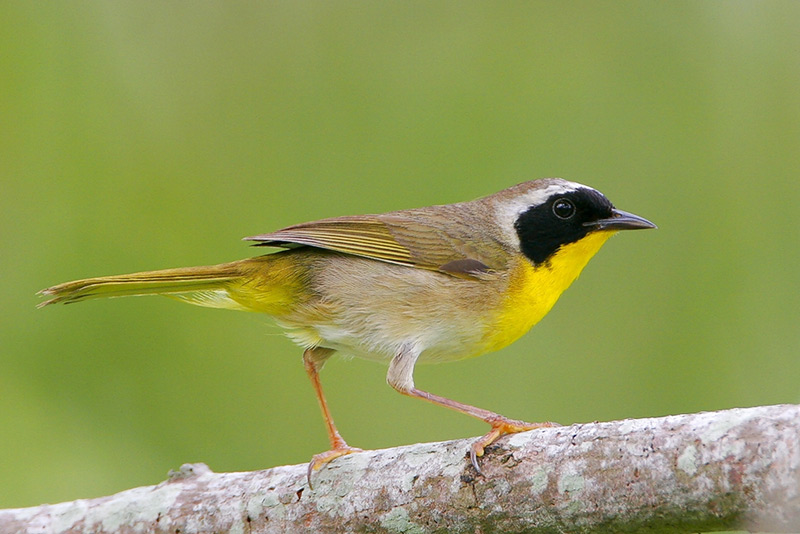

Photograph © Greg Lavaty.
Scientific name: Geothlypis trichas
Length: 5 inches
Weight: .35 ounces
Wingspan: 6.75 inches
Song: “witchey..witchety..witchety!”
The Common Yellowthroat is a small, olive-brown warbler with a yellow throat and undertail. Males have a black mask with a pale border on part of it.
Females are plainer and lack the black mask. Instead, they have a hint of a pale eyering. Both sexes have pale brown flanks, rounded wings, and a rounded tail.
Common Yellowthroats feed on insects and spiders that they find in low, wet, dense vegetation. They forage by picking food items from leaves and stems.
The Common Yellowthroat makes a loose and bulky, well-hidden cup nest out of grass and other plant matter. The female builds the nest on or close to the ground in dense grassy or marshy vegetation.
This warbler species frequents low, wet tangles, the grassy edges of creeks and rivers, and other marshy vegetation. It is a summer resident over a large part of Canada and the USA. This species also winters in California and the southeastern USA.
Key Identifications:
- Small warbler with a yellow throat and undertail. Males have black masks, females are plain olive-brown and have a hint of an eyering.
- Forages for insects in low, wet, dense vegetation.
- Makes a loose, bulky, well-hidden cup nest on or near the ground.
- Males sing a friendly, warbled, “witchey..witchety..witchety!”. Both sexes also make a short, “jerrt!” call.
Red-bellied Woodpecker
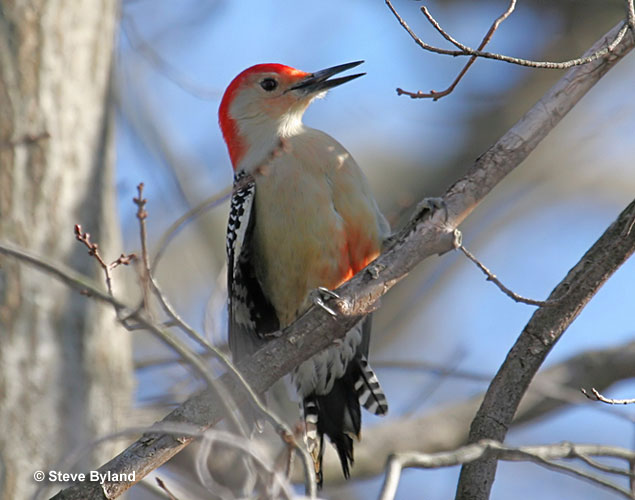

Scientific name: Melanerpes carolinus
Length: 9.25 inches
Weight: 2.2 ounces
Wingspan: 16 inches
Song: “Qwerr!”
Red-bellied Woodpeckers are medium-sized with black and white barring on their back and wings. They have a long beak and pale gray underparts with a small red patch on the belly.
Males have red on the head from the bill to the back of the neck (the nape). Females have an orange-red spot above their bill and red on the back of their head. Both sexes have a mostly white rump and central tail feathers.
This woodpecker species has long wings and “undulating” flight, where it moves up and down as it flies. In flight, Red-bellied Woodpeckers show a small white patch in their wings.
The Red-bellied Woodpecker lives in wooded habitats. It eats nuts, seeds, insects, fruit, and can attack nestlings of other species. It also visits bird feeders.
This striking woodpecker occurs in pairs and nests in tree cavities high above the ground. It is common in the eastern USA and parts of southern Ontario.
Key Identifications:
- Grayish woodpecker with black and white barring above, and red on the top of the head and back of the neck.
- Forages for seeds, nuts, insects and other food on trunks and branches.
- Nests in a tree cavity, high overhead.
- Makes a loud exclamation, “Qwerr!“. It also makes other, briefer and quieter “chug” calls.
White-throated Sparrow
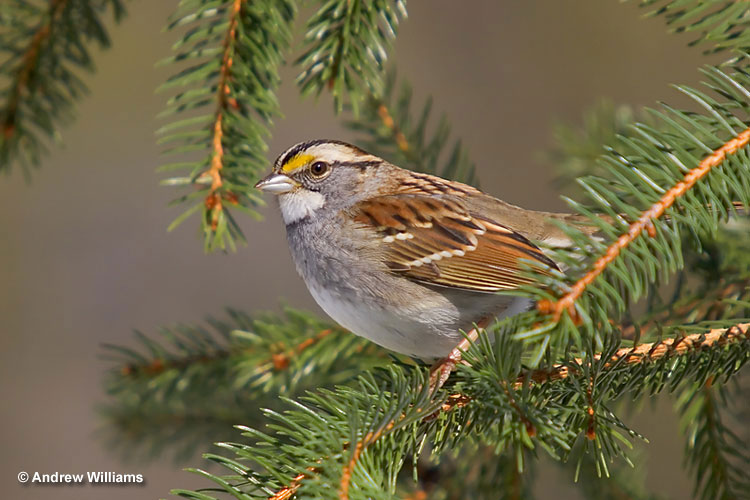

Scientific name: Zonotrichia albicollis
Length: 6.75 inches
Weight: .91 ounces
Wingspan: 9 inches
Song: “Ohhh Canada Canada Canada”
The White-throated Sparrow is a chunky, gray and brown sparrow with a white throat and black and white stripes on its head. It has dark streaks on its back, a gray rump, and a bit of yellow in front of its eyes.
Males and females look the same and have reddish-brown wings with two white wing bars. Young White-throated Sparrows and some adults are duller brown with tan stripes on their heads and a dingy white throat.
White-throated Sparrows forage for seeds and insects on the ground, and also eat fruits in short trees and bushes. They reveal hidden food items by using their feet to scratch and kick away leaves.
This sparrow breeds in northern forests and builds a cup nest with grass and twigs. They construct the nest at the edge of forest, on or close to the ground, in dense vegetation.
These sparrows usually occur in flocks and winter in the eastern and southwestern USA and parts of California.
Key Identifications:
- Large sparrow with a white throat and bold black and white or tan stripes on its head.
- Scratches leaves on the ground to find seeds and insects. They also eat berries.
- Makes a cup nest of grass, bark, and twigs, on the ground, under dense vegetation.
- Flocks of White-throated Sparrows often make sharp “tink” calls. They also sing a clear, whistled song, “Ohhh Canada Canada Canada” or, “Ohhh, Cana, Cana, Cana”.
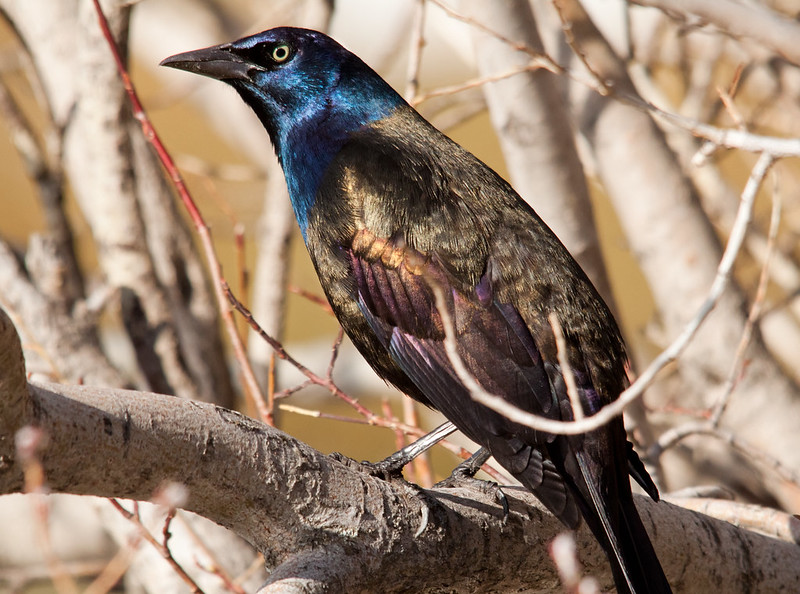
Common Grackle

© Shawn McCready
Scientific name: Quiscalus quiscula
Length: 12.5 inches
Weight: 4 ounces
Wingspan: 17 inches
Song: “Sherink!”
The Common Grackle is a jay-sized, glossy black bird with pale eyes and a long, wedge-shaped tail. Depending on lighting, this bird shows metallic purple, blue, green, and bronze highlights.
Males and females look very similar, but females have shorter tails and less iridescence. Both sexes also have stout, black beaks and strong, black legs and feet.
In flight, Common Grackles move up and down as they move through the air. They usually flock together and often forage in farm fields, on lawns, and in other open habitats.
These omnivores feed on a variety of items, including insects, seeds, grain, small animals, garbage, and the eggs and nestlings of other birds.
Common Grackles build bulky stick nests, usually in conifers in woodlands, parks, near water, and urban areas.
This species can form big flocks in the winter and lives in a variety of semi-open and open habitats in eastern Canada and the eastern USA.
Key Identifications:
- Fairly large, black bird with glossy purple, greenish, bronze, or dark blue highlights. It also has pale eyes and a long, wedge-shaped tail.
- Forages for insects, seeds, and other food on the ground in a variety of open habitats.
- Constructs a bulky cup nest in a conifer.
- Common Grackles are vocal birds. They frequently give raspy, metallic calls, “Sherink!”, and “kek” calls.
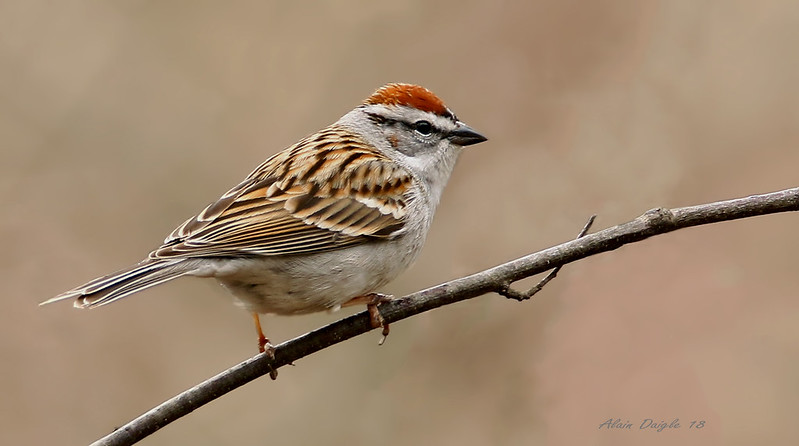
Chipping Sparrow

© Alain Daigle
Scientific name: Spizella passerina
Length: 5.5 inches
Weight: .42 ounces
Wingspan: 8.5 inches
Song: “titititititititititititti”
The Chipping Sparrow is a small, brown and gray sparrow with a longish, slightly forked tail and a conical bill. In summer, it has a rufous cap, white eyebrow, and dark lines through each eye.
In fall and winter, Chipping Sparrows are duller, have brown and buff heads, a gray rump, and a dark line through their eyes.
This species forages on the ground for insects and small seeds in open, grassy areas near conifers.
Chipping Sparrows use grass, hair, and other materials to make a cup nest low in a bush or small tree.
These sparrows live in parks, open woodlands, and on golf courses in much of Canada, most of the USA, and parts of Mexico.
Key Identifications:
- Small, slender sparrow with a rufous cap and white eyebrow in summer and a brown and buff head, gray rump, and dark line through their eyes in the winter.
- Forages for insects and seeds on the ground in grassy habitats with pines.
- Uses grass and animal hair to make an open cup nest low in a bush or small tree.
- Makes short chip notes and has a mechanical sounding, trilled song, “titititititititititititti”.
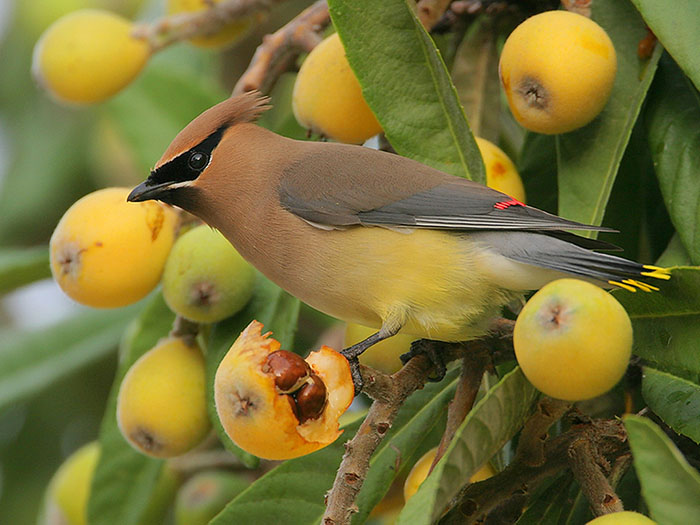
Cedar Waxwing

Scientific name: Bombycilla cedrorum
Length: 7.25 inches
Weight: 1.1 ounces
Wingspan: 12 inches
Song: “sree…zree!”
The Cedar Waxwing is a thrush-sized, crested bird with a black mask, black throat, and sleek, pale brown, gray, and yellow plumage. Both sexes look similar and have bright yellow on the tip of their tail, and a pale yellow belly.
Young birds are grayish-brown with some thick streaks on white underparts. Adult Cedar Waxwings also have a few small red dots on their wings, and have a white undertail.
This species feeds on insects and small fruits. In summer, waxwings often sally into the air to catch bugs in flight. However, they mostly feed on berries and forage for them in large flocks, especially in the winter.
The Cedar Waxwing constructs a bulky, open cup nest out of moss, flowers, bark, other bits of plants, and other materials. It builds its nest in an isolated tree or bush.
Cedar Waxwings breed in a large area of Canada and occur in the northern half of the USA, making it one of the most common birds of Vermont.
Key Identifications:
- Sleek, pale brown and gray crested bird with a black mask, black throat, and a bright yellow tip on its tail.
- Catches insects in flight and visits fruiting and trees and bushes to feed on berries.
- Uses bark and other materials to make an open cup nest in an isolated tree or bush.
- Cedar Waxwings are very vocal and often make a soft, whispering call, “sree…zree!”.
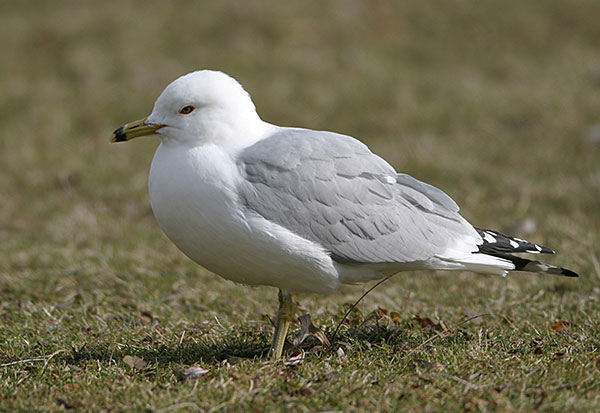
Ring-billed Gull

Scientific name: Larus delawarensis
Length: 17.5 inches
Weight: 1.1 pound
Wingspan: 48 inches
Song: “KLEE..KLEEE..kleeya,kleeya,kleeya”
The Ring-billed Gull is a medium-sized pale gray and white gull with a black ring around its yellowish beak. Males and females look the same and have yellowish legs and feet, pale eyes, and black wing tips with a few white spots.
These gulls have a direct, fairly quick flight with leisurely wing beats. Young birds have pink and black bills, a white tail with a black tip, and mottled black and gray wings.
Ring-billed Gulls are scavengers and opportunists that feed on carrion, fish, worms, small animals, grain, and other food items.
They usually occur in flocks that roam lakes, rivers, urban areas, and other habitats in search of feeding opportunities. The Ring-billed Gull breeds in colonies, often on islands, and makes a shallow stick nest on the ground.
This gull species occurs not only in Vermont, but also in many parts of Canada and the USA south to Central America.
Key Identifications:
- Medium-sized pale gray and white gull with a black ring on its bill and yellow legs and feet. Juveniles have pink and black beaks.
- Forages for fish, carrion, and many other food items in wetlands and open habitats.
- Nests on the ground, in colonies.
- Ring-billed Gulls often call. In flight, they often make a high-pitched “kleea” sound. On the ground, displaying birds make a loud, laughing, “KLEE..KLEEE..kleeya,kleeya,kleeya”.
Birds of Vermont – Frequently Asked Questions
What birds are common in Vermont?
Lots of woodland and forest birds are common in Vermont. Some of the most common species are the Black-capped Chickadee, American Crow, Blue Jay, and American Goldfinch.
What is the most common bird in Vermont?
The most common bird in Vermont is the Black-capped Chickadee. This small bird species is seen more than any other species in the state.
How many species of birds are in Vermont?
In total, 388 species of birds are in Vermont. This is the number of species that have been found in the state.
What is the state bird of Vermont?
Vermont’s state bird is the Hermit Thrush. This small thrush was chosen as the state symbol back in 1941.
What is the bright yellow bird in Vermont?
The bright yellow bird in Vermont is an American Goldfinch, or a Yellow Warbler. Both of these species are common, frequently seen birds in Vermont.
What are the bright blue birds in Vermont?
The bright blue birds in Vermont are male Indigo Buntings. These beautiful little birds are common throughout the state.
Does Vermont have Eagles?
Yes, Vermont has eagles. Bald Eagles and rarer Golden Eagles live in the state.

